Treatment with milk fat globule epidermal growth factor-factor 8 (MFG-E8) reduces inflammation and lung injury in neonatal sepsis
- PMID: 28343695
- PMCID: PMC5513803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.02.006
Treatment with milk fat globule epidermal growth factor-factor 8 (MFG-E8) reduces inflammation and lung injury in neonatal sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis remains one of the leading causes of infant death worldwide. It is characterized by uncontrolled inflammatory responses due to proven bacterial infection. Despite improvement in supportive care and the availability of effective antibiotics, no specific therapy targeting the dysregulated inflammatory response is available for neonatal sepsis. Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor-factor 8 (MFG-E8) is a secretory glycoprotein abundantly present in human milk. MFG-E8 suppresses the systemic inflammatory responses in adult murine injury models by improving the clearance of dying cells. We hypothesized that exogenous administration of recombinant mouse MFG-E8 could inhibit the exaggerated inflammatory response and lung injury in a murine model of neonatal sepsis.
Methods: Neonatal sepsis was induced in 5- to 7-day-old male and female C57BL6 mice using an intraperitoneal injection of cecal slurry. At 1 hour after sepsis induction, a single dose of 40 μg/kg recombinant mouse MFG-E8 or vehicle was administered via retro-orbital injection. All neonates were returned to their mothers as a group. At 10 hours after cecal slurry injection, pups were killed and blood and lung tissues were collected. Control mice underwent a similar procedure with the exception of cecal slurry intraperitoneal injection.
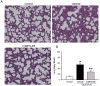
Results: Serum lactate dehydrogenase, IL-1β, and IL-6 were significantly increased 10 hours after cecal slurry injection. Treatment with recombinant mouse MFG-E8 decreased these levels by 30%, 56%, and 37%, respectively. Lung morphology was significantly compromised in the vehicle group after cecal slurry injection, whereas the recombinant mouse MFG-E8-treated groups demonstrated a 48% improvement in the lung injury score. Lung IL-6 and MIP-2 protein levels were significantly reduced with recombinant mouse MFG-E8 treatment. Lung neutrophil infiltration as observed by Gr-1 staining and, TUNEL-positive cells were also significantly reduced with recombinant mouse MFG-E8 treatment.
Conclusion: Treatment with recombinant mouse MFG-E8 attenuated inflammation and lung injury in murine neonatal sepsis. Thus, MFG-E8 could be developed as a possible therapy for neonatal sepsis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
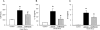
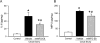
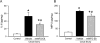
Similar articles
-
Deficiency in milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor-factor 8 exacerbates organ injury and mortality in neonatal sepsis.J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Sep;52(9):1520-1527. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.12.022. Epub 2016 Dec 30. J Pediatr Surg. 2017. PMID: 28081854 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel MFG-E8-derived Oligopeptide, MOP3, Improves Outcomes in a Preclinical Murine Model of Neonatal Sepsis.J Pediatr Surg. 2024 Jul;59(7):1282-1290. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2024.03.025. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Pediatr Surg. 2024. PMID: 38582704
-
Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor-factor VIII attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.J Surg Res. 2017 Jun 1;213:281-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.02.024. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28601327 Free PMC article.
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor VIII in sepsis and ischemia-reperfusion injury.Mol Med. 2011 Jan-Feb;17(1-2):126-33. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00135. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20882259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of MFG-E8 as a novel therapeutic target for diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Nov;17(11):1275-85. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.829455. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23972256 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Analysis of Microarray Studies to Identify Novel Diagnostic Markers in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis with Hunner Lesion.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Mar 19;15:3143-3154. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S351287. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35342305 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Clinically-Relevant Experimental Models of Neonatal Shock and Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Shock. 2020 May;53(5):596-604. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001507. Shock. 2020. PMID: 31977960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent CTLs can be induced against tumor cells in an environment of lower levels of systemic MFG-E8.Cancer Sci. 2024 Apr;115(4):1114-1128. doi: 10.1111/cas.16099. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38332689 Free PMC article.
-
MFGE8 promotes adult hippocampal neurogenesis in rats following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage via modifying the integrin β3/Akt signaling pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Aug 11;10(1):359. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02132-x. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39128910 Free PMC article.
-
Guanxinkang Decoction Attenuates the Inflammation in Atherosclerosis by Regulating Efferocytosis and MAPKs Signaling Pathway in LDLR-/- Mice and RAW264.7 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 7;12:731769. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.731769. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34950025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, Perin J, Scott S, Lawn JE, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379:2151–61. - PubMed
-
- Lim JC, Golden JM, Ford HR. Pathogenesis of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2015;31:509–18. - PubMed
-
- Verani JR, McGee L, Schrag SJ, Division of Bacterial Diseases NCfI, Respiratory Diseases CfDC, Prevention Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease–revised guidelines from CDC, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59:1–36. - PubMed
-
- Oeser C, Lutsar I, Metsvaht T, Turner MA, Heath PT, Sharland M. Clinical trials in neonatal sepsis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68:2733–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

