Comprehensive Cell Surface Protein Profiling Identifies Specific Markers of Human Naive and Primed Pluripotent States
- PMID: 28343983
- PMCID: PMC5459756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.02.014
Comprehensive Cell Surface Protein Profiling Identifies Specific Markers of Human Naive and Primed Pluripotent States
Abstract
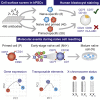
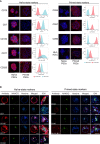
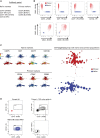
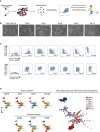
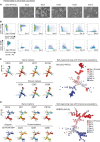
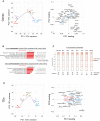
Human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) exist in naive and primed states and provide important models to investigate the earliest stages of human development. Naive cells can be obtained through primed-to-naive resetting, but there are no reliable methods to prospectively isolate unmodified naive cells during this process. Here we report comprehensive profiling of cell surface proteins by flow cytometry in naive and primed human PSCs. Several naive-specific, but not primed-specific, proteins were also expressed by pluripotent cells in the human preimplantation embryo. The upregulation of naive-specific cell surface proteins during primed-to-naive resetting enabled the isolation and characterization of live naive cells and intermediate cell populations. This analysis revealed distinct transcriptional and X chromosome inactivation changes associated with the early and late stages of naive cell formation. Thus, identification of state-specific proteins provides a robust set of molecular markers to define the human PSC state and allows new insights into the molecular events leading to naive cell resetting.
Keywords: antibody library; blastocyst; cell surface markers; differentiation; embryonic stem cells; pluripotency; reprogramming.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Surface Markers Guide the Journey toward Naive Pluripotency.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Jun 1;20(6):737-738. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.05.004. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 28575685
References
-
- Brandenberger R., Wei H., Zhang S., Lei S., Murage J., Fisk G.J., Li Y., Xu C., Fang R., Guegler K. Transcriptome characterization elucidates signaling networks that control human ES cell growth and differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:707–716. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter M.K., Rosler E.S., Fisk G.J., Brandenberger R., Ares X., Miura T., Lucero M., Rao M.S. Properties of four human embryonic stem cell lines maintained in a feeder-free culture system. Dev. Dyn. 2004;229:243–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

