A Genome-wide Analysis of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells in 2D or 3D Culture
- PMID: 28343999
- PMCID: PMC5390115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.02.014
A Genome-wide Analysis of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells in 2D or 3D Culture
Abstract
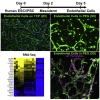
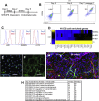
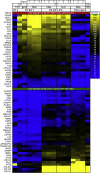
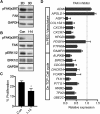
A defined protocol for efficiently deriving endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells was established and vascular morphogenesis was used as a model system to understand how synthetic hydrogels influence global biological function compared with common 2D and 3D culture platforms. RNA sequencing demonstrated that gene expression profiles were similar for endothelial cells and pericytes cocultured in polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrogels or Matrigel, while monoculture comparisons identified distinct vascular signatures for each cell type. Endothelial cells cultured on tissue-culture polystyrene adopted a proliferative phenotype compared with cells cultured on or encapsulated in PEG hydrogels. The proliferative phenotype correlated to increased FAK-ERK activity, and knockdown or inhibition of ERK signaling reduced proliferation and expression for cell-cycle genes while increasing expression for "3D-like" vasculature development genes. Our results provide insight into the influence of 2D and 3D culture formats on global biological processes that regulate cell function.
Keywords: 3D culture; MAPK; Matrigel; differentiation; endothelial cells; focal adhesion kinase; human pluripotent stem cells; hydrogel; tissue engineering; xeno-free.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn N.G., Seger R., Bratlien R.L., Diltz C.D., Tonks N.K., Krebs E.G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:4220–4227. - PubMed
-
- Arnaoutova I., George J., Kleinman H.K., Benton G. The endothelial cell tube formation assay on basement membrane turns 20: state of the science and the art. Angiogenesis. 2009;12:267–274. - PubMed
-
- Bauer J., Margolis M., Schreiner C., Edgell C.J., Azizkhan J., Lazarowski E., Juliano R.L. In vitro model of angiogenesis using a human endothelium-derived permanent cell line—contributions of induced gene expression, G-proteins, and integrins. J. Cell Physiol. 1992;153:437–449. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

