The KIF1A homolog Unc-104 is important for spontaneous release, postsynaptic density maturation and perisynaptic scaffold organization
- PMID: 28344334
- PMCID: PMC5366810
- DOI: 10.1038/srep38172
The KIF1A homolog Unc-104 is important for spontaneous release, postsynaptic density maturation and perisynaptic scaffold organization
Abstract
The kinesin-3 family member KIF1A has been shown to be important for experience dependent neuroplasticity. In Drosophila, amorphic mutations in the KIF1A homolog unc-104 disrupt the formation of mature boutons. Disease associated KIF1A mutations have been associated with motor and sensory dysfunctions as well as non-syndromic intellectual disability in humans. A hypomorphic mutation in the forkhead-associated domain of Unc-104, unc-104bris, impairs active zone maturation resulting in an increased fraction of post-synaptic glutamate receptor fields that lack the active zone scaffolding protein Bruchpilot. Here, we show that the unc-104brismutation causes defects in synaptic transmission as manifested by reduced amplitude of both evoked and miniature excitatory junctional potentials. Structural defects observed in the postsynaptic compartment of mutant NMJs include reduced glutamate receptor field size, and altered glutamate receptor composition. In addition, we observed marked loss of postsynaptic scaffolding proteins and reduced complexity of the sub-synaptic reticulum, which could be rescued by pre- but not postsynaptic expression of unc-104. Our results highlight the importance of kinesin-3 based axonal transport in synaptic transmission and provide novel insights into the role of Unc-104 in synapse maturation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
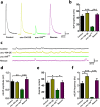

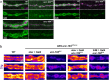
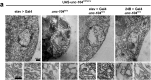
References
-
- Hirokawa N., Noda Y., Tanaka Y. & Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 682–96 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N. & Tanaka Y. Kinesin superfamily proteins (KIFs): Various functions and their relevance for important phenomena in life and diseases. Exp Cell Res 334, 16–25 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N., Nitta R. & Okada Y. The mechanisms of kinesin motor motility: lessons from the monomeric motor KIF1A. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 877–84 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Hall D. H. & Hedgecock E. M. Kinesin-related gene unc-104 is required for axonal transport of synaptic vesicles in C. elegans. Cell 65, 837–47 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Otsuka A. J. et al. The C. elegans unc-104 gene encodes a putative kinesin heavy chain-like protein. Neuron 6, 113–22 (1991). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

