The prevalence extent of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) use among Saudis
- PMID: 28344484
- PMCID: PMC5357106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.09.009
The prevalence extent of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) use among Saudis
Abstract
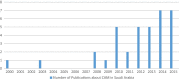
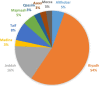
Introduction: There is worldwide interest in the use of CAM. Studying CAM in Saudi population is important as it will reflect the influence of psychosocial, cultural and religious factors on health beliefs and behaviors. The objective of this study was to present an updated review on the use of CAM practices in Saudi Arabia including commonly used types, common conditions for which it has been used and who uses CAM. Methods: This review used data from national surveys conducted in Saudi Arabia and published between 2000 and 2015. The literature search was performed considering standards adopted such as Moose guidelines for observational studies. Two authors independently reviewed each article. The search yielded 73 articles, and a total of 36 articles were included. Further careful data extraction was carried out by two independents reviewers. Results: Most of the reviewed studies were cross-sectional in design and were published between 2014 and 2015, and mostly in Riyadh region. Substantial difference in the findings for the patterns of CAM use was revealed. The most commonly employed practice was of spiritual type such as prayer and reciting Quran alone or on water. Other types include herbs (8-76%), honey (14-73%) and dietary products (6-82%). Cupping (Alhijamah) was least used (4-45%). Acupuncture was more practiced among professionals. Conclusion: The utilization of CAM is widely practiced in Saudi Arabia. There is need for efforts to promote research in the field of CAM to address each practice individually. Population surveys should be encouraged supported by mass media to raise knowledge and awareness about the practice of different CAM modalities. The national center of CAM should play a major role in these efforts.
Keywords: CAM, Complementary and Alternative Medicine; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CSS, cross-sectional study; Cupping; Herbs; ICM, integrative and complementary medicine; Integrative complementary therapies; NA, not applicable; RCT, randomized control trial; SA, Saudi Arabia; Saudi Arabia; Spiritual.
Figures
References
-
- Abd El-Mawla A.M.A., Albarrag A.R., Abdallah M.A.K. Herbal medicine use in a group Taif children, Saudi Arabia. Spatula DD. 2013;3(2):41–44.
-
- Abd El-Mawla A.M.A., Magd M.S.M., Mahran S.S. Prevalence and indication of herbal medicine in digestive system disorders in Al-Taif area, Saudi Arabia. Spatula DD. 2014;4(3):127–130.
-
- Abd El-Mawla A.A.A., Albarrag A.A., Abdallah M.A. Use of herbal pharmaceutical products in Al-Taif area, Saudi Arabia: prevalence and indication. Spatula DD. 2014;4(3):151–158.
-
- Al Mansour M.A., Al-Bedah A.M., AlRukban M.O., Elsubai I.S., Mohamed E.Y., El Olemy A.T., Khalil A.A., Khalil M.K., Alqaed M.S., Almudaiheem A. Medical students’ knowledge, attitude, and practice of complementary and alternative medicine: a pre-and post-exposure survey in Majmaah University, Saudi Arabia. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 2015;6:407–420. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Mansour M.A., Mohammad E.Y., Abdalla S., Medani K., Mahmoud W., Meraj S. Satisfaction, self-use and perception of medical students in Majmaah University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, towards complementary and alternative medicine. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2015;10(1):74–78.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

