Direct and enhanced delivery of nanoliposomes of anti schizophrenic agent to the brain through nasal route
- PMID: 28344488
- PMCID: PMC5357100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.07.003
Direct and enhanced delivery of nanoliposomes of anti schizophrenic agent to the brain through nasal route
Abstract
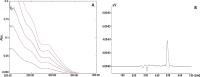
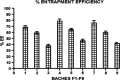
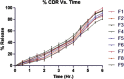
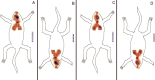
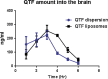
The problem of inadequate oral bioavailability of Quetiapine Fumarate, a lipophilic drug used for schizophrenia, due to hepatic metabolism and repulsion by brain barrier was attempted in this study. Combination of two approaches, viz. Quetiapine inclusion into the liposomal carrier for better diffusion and administration through nasal route to avoid hepatic metabolism and barrier elimination was applied. Thin film hydration followed by sonication method was employed in liposome preparation and the formulation was optimized using 32 full factorial design. The number of sonication cycles (X1) of 2 min and 80% amplitude and molar ratio of constructional components such as cholesterol to egg phosphatidylcholine (X2) as independent variables and a % of entrapment efficiency (Y1) and cumulative in vitro drug release (Y2) at 6 h as dependent variables was selected. Batch F7 prepared by 2 cycles of sonication and 1:3 M ratio of cholesterol:egg phosphatidylcholine was optimized as a consequence of substantial entrapment efficiency of 75.63 ± 3.77%, and 99.92 ± 1.88% drug release and 32.33 ± 1.53% drug diffusion, which was optimum among all other batches at 6 h. Diffusion study was done for all the batches of liposomal formulation by using sheep nasal mucosa and good amount with better diffusion rate was measured which proved liposomal dispersion a virtuous delivery system for brain drug delivery through nasal route. Results of in vivo, ciliotoxicity and gamma scintigraphy studies on mice supported the above inference.
Keywords: Blood brain barrier; Dispersion; Liposomes; Nasal route; Quetiapine Fumarate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparative study between simple and optimized liposomal dispersion of quetiapine fumarate for diffusion through nasal route.Drug Deliv. 2016 May;23(4):1214-21. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2015.1120364. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26643946
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Niosomal in situ Nasal Gel of a Serotonin Receptor Agonist, Buspirone Hydrochloride for the Brain Delivery via Intranasal Route.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018;6(1):69-78. doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180130105919. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29380709
-
"Application of Box-Behnken design for optimization and development of quetiapine fumarate loaded chitosan nanoparticles for brain delivery via intranasal route* ".Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Aug;89:206-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.076. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 27130654
-
Intranasal Delivery of Darunavir-Loaded Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel: Experimental Design, In Vitro Evaluation, and Pharmacokinetic Studies.Gels. 2022 May 30;8(6):342. doi: 10.3390/gels8060342. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35735686 Free PMC article.
-
Topical liposomal gel of idoxuridine for the treatment of herpes simplex: pharmaceutical and clinical implications.Pharm Dev Technol. 2004 Aug;9(3):277-89. doi: 10.1081/pdt-200031432. Pharm Dev Technol. 2004. PMID: 15458233 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics study of chitosan-coated liposomes containing sumatriptan in the treatment of migraine.Caspian J Intern Med. 2022 Winter;13(1):90-99. doi: 10.22088/cjim.13.1.90. Caspian J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35178213 Free PMC article.
-
Nano Carrier Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Advantages and Limitations.Molecules. 2020 Nov 13;25(22):5294. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225294. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33202839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of exogenous 6-BA and NAA on growth and contents of medicinal ingredient of Phellodendron chinense seedlings.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Sep;25(6):1189-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.037. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30174521 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology-based Nose-to-brain Delivery in Epilepsy: A NovelApproach to Diagnosis and Treatment.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024;12(4):314-328. doi: 10.2174/0122117385265554230919070402. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37818558 Review.
-
Surface-tailoring of emulsomes for boosting brain delivery of vinpocetine via intranasal route: in vitro optimization and in vivo pharmacokinetic assessment.Drug Deliv. 2022 Aug 8;29(1):2671-2684. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2110996. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35975309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aacharya S.P., Pundarikakshudu K., Upadhyay P., Shelat P., Lalwani A. Development of phenytoin intranasal microemulsion for treatment of epilepsy. J. Pharma. Invest. 2015;45(4):375–384.
-
- Abbott N.J., Romero I.A. Transporting therapeutics across the blood brain barrier. Mol. Med. 1996;2:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Afergan E., Epstein H., Dahan R., Koroukhov N., Rohekar K., Danenberg H.D. Delivery of serotonin to the brain by monocytes following phagocytosis of liposomes. J. Control. Release. 2008;132:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Alsarra I.A., Hamed A.Y., Alanazi F.K. Acyclovir liposomes for intranasal systemic delivery: development and pharmacokinetics evaluation. Drug Delivery. 2008;15(5):313–321. - PubMed
-
- Alsarra I.A., Hamed A.Y., Alanazi F.K., Maghraby G.M. In: Drug Delivery to the Central Nervous System. sixth ed. Jain K.K., editor. Springer Science & Business Media; 2010. Vesicular systems for intranasal drug delivery; pp. 175–203.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

