Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Limits Angiotensin II-Induced DNA Oxidation and Protein Nitration in Humans
- PMID: 28344559
- PMCID: PMC5344903
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00138
Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Limits Angiotensin II-Induced DNA Oxidation and Protein Nitration in Humans
Abstract
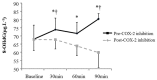
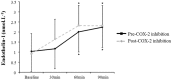
Compared to other cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, celecoxib is associated with a lower cardiovascular risk, though the mechanism remains unclear. Angiotensin II is an important mediator of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of vascular disease. Cyclooxygenase-2 may modify the effects of angiotensin II though this has never been studied in humans. The purpose of the study was to test the effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on plasma measures of oxidative stress, the vasoconstrictor endothelin-1, and nitric oxide metabolites, both at baseline and in respose to Angiotensin II challenge in healthy humans. Measures of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, advanced oxidation protein products, nitrotyrosine, endothelin-1, and nitric oxide metabolites were assessed from plasma samples drawn at baseline and in response to graded angiotensin II infusion (3 ng/kg/min × 30 min, 6 ng/kg/min × 30 min) before and after 14 days of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in 14 healthy subjects (eight male, six female) in high salt balance, a state of maximal renin angiotensin system suppression. Angiotensin II infusion significantly increased plasma oxidative stress compared to baseline (8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine; +17%; advanced oxidation protein products; +16%), nitrotyrosine (+76%). Furthermore, levels of endothelin-1 levels were significantly increased (+115%) and nitric oxide metabolites were significantly decreased (-20%). Cycloxygenase-2 inhibition significantly limited the increase in 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, nitrotyrosine and the decrease in nitric oxide metabolites induced by angiotensin II infusion, though no changes in advanced oxidation protein products and endothelin-1 concentrations were observed. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with celecoxib partially limited the angiotensin II-mediated increases in markers of oxidative stress in humans, offering a potential physiological pathway for the improved cardiovascular risk profile of this drug.
Keywords: blood pressure; celecoxib; cycloxygenase-2 inhibition; endothelin-1; humans; nitric oxide; oxidative stress; renin-angiotensin system.
Figures
References
-
- Channick R. N., Simonneau G., Sitbon O., Robbins I. M., Frost A., Tapson V. F., et al. (2001). Effects of the dual endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet 358, 1119–1123. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06250-X - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

