Reslizumab and Eosinophilic Asthma: One Step Closer to Precision Medicine?
- PMID: 28344579
- PMCID: PMC5344894
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00242
Reslizumab and Eosinophilic Asthma: One Step Closer to Precision Medicine?
Abstract
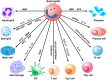
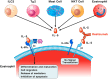
Human eosinophils represent approximately 1% of peripheral blood leukocytes. However, these cells have the propensity to leave the blood stream and migrate into inflamed tissues. Eosinophilic inflammation is present in a significant proportion of patients with severe asthma. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects more than 315 million people worldwide, with 10% having severe uncontrolled disease. Although the majority of patients can be efficiently treated, severe asthmatics continue to be uncontrolled and are at risk of exacerbations and even death. Interleukin-5 (IL-5) plays a fundamental role in eosinophil differentiation, maturation, activation and inhibition of apoptosis. Therefore, targeting IL-5 is an appealing approach to the treatment of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. Reslizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody, binds with high affinity to amino acids 89-92 of IL-5 that are critical for binding to IL-5 receptor α. Two phase III studies have demonstrated that reslizumab administration in adult patients with severe asthma and eosinophilia (≥400 cells/μL) improved lung function, asthma control, and symptoms. Thus, the use of blood eosinophils as a baseline biomarker could help to select patients with severe uncontrolled asthma who are likely to achieve benefits in asthma control with reslizumab. In conclusion, targeted therapy with reslizumab represents one step closer to precision medicine in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.
Keywords: IL-5 receptor; anti-IL-5; asthma; eosinophils; interleukin-5; reslizumab.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

