HLA class II antigen-processing pathway in tumors: Molecular defects and clinical relevance
- PMID: 28344859
- PMCID: PMC5353941
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1171447
HLA class II antigen-processing pathway in tumors: Molecular defects and clinical relevance
Abstract
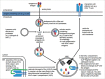
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II antigen-processing machinery (APM) presents to cognate CD4+ T-cells antigenic peptides mainly generated from exogeneous proteins in the endocytic compartment. These CD4+ T cells exert helper function, but may also act as effector cells, thereby recognizing HLA class II antigen-expressing tumor cells. Thus, HLA class II antigen expression by tumor cells influences the tumor antigen (TA)-specific immune responses and, depending on the cancer type, the clinical course of the disease. Many types of human cancers express HLA class II antigens, although with marked differences in their frequency. Some types of cancer lack HLA class II antigen expression, which could be due to structural defects or deregulation affecting different components of the complex HLA class II APM and/or from lack of cytokine(s) in the tumor microenvironment. In this review, we have summarized the information about HLA class II antigen distribution in normal tissues, the structural organization of the HLA class II APM, their expression and regulation in malignant cells, the defects, which have been identified in malignant cells, and their functional and clinical relevance.
Keywords: Antigen-processing; HLA class II; immune response, tumor.
Figures
References
-
- Jensen PE. Recent advances in antigen processing and presentation. Nat Immunol 2007; 8:1041-8; PMID:17878914; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ni1516 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vyas JM, Van der Veen AG, Ploegh HL. The known unknowns of antigen processing and presentation. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8:607-18; PMID:18641646; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri2368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garrido F, Algarra I, Garcia-Lora AM. The escape of cancer from T lymphocytes: immunoselection of MHC class I loss variants harboring structural-irreversible “hard” lesions. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010; 59:1601-6; PMID:20625726; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00262-010-0893-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bukur J, Jasinski S, Seliger B. The role of classical and non-classical HLA class I antigens in human tumors. Semin Cancer Biol 2012; 22:350-8; PMID:22465194; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.03.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campoli M, Ferrone S. HLA antigen and NK cell activating ligand expression in malignant cells: a story of loss or acquisition. Semin Immunopathol 2011; 33:321-34; PMID:21523560; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00281-011-0270-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
