Reduction of postprandial glucose by lixisenatide vs sitagliptin treatment in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes on background insulin glargine: A randomized phase IV study (NEXTAGE Study)
- PMID: 28345162
- PMCID: PMC5573929
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.12945
Reduction of postprandial glucose by lixisenatide vs sitagliptin treatment in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes on background insulin glargine: A randomized phase IV study (NEXTAGE Study)
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the pharmacodynamics of lixisenatide once daily vs sitagliptin once daily in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes receiving insulin glargine U100.
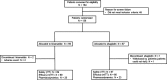
Materials and methods: This multicentre, open-label, phase IV study (NEXTAGE Study; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02200991) randomly assigned 136 patients to either lixisenatide once daily via subcutaneous injection (10 µg initially increased weekly by 5 up to 20 µg) or once-daily oral sitagliptin 50 mg. The primary endpoint was the change in postprandial glucose (PPG) exposure 4 hours after a standardized breakfast (PPG area under the plasma glucose concentration-time curve [AUC0:00-4:00h ]) from baseline to day 29.
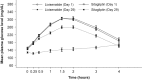
Results: Lixisenatide reduced PPG exposure to a statistically significantly greater extent than sitagliptin: least squares (LS) mean change from baseline in PPG AUC0:00-4:00h was -347.3 h·mg/dL (-19.3 h·mmol/L) in the lixisenatide group and -113.3 h·mg/dL (-6.3 h·mmol/L) in the sitagliptin group (LS mean between-group difference -234.0 h·mg/dL [-13.0 h·mmol/L], 95% confidence interval -285.02 to -183.00 h·mg/dL [-15.8 to -10.2 h·mmol/L]; P < .0001). Lixisenatide led to significantly greater LS mean reductions in maximum PPG excursion than sitagliptin (-122.4 vs -46.6 mg/dL [-6.8 vs -2.6 h·mmol/L]; P < .0001). Change-from-baseline reductions in exposure to C-peptide, fasting glycoalbumin levels, and the gastric emptying rate were greater in the lixisenatide than in the sitagliptin group. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was higher with lixisenatide (60.9%) than with sitagliptin (16.4%), with no serious events or severe hypoglycaemia reported.
Conclusion: Lixisenatide reduced PPG significantly more than sitagliptin, when these agents were added to basal insulin glargine U100, and was well tolerated.
Keywords: gastric emptying; glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; lixisenatide; postprandial glucose; randomized trial; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamic characteristics of lixisenatide once daily versus liraglutide once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled on metformin.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Jul;15(7):642-9. doi: 10.1111/dom.12076. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013. PMID: 23368510 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide in a predominantly Asian population with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled with basal insulin: The GetGoal-L-C randomized trial.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Feb;20(2):335-343. doi: 10.1111/dom.13072. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 28742225 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of semaglutide once weekly vs sitagliptin once daily, both as monotherapy in Japanese people with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Feb;20(2):378-388. doi: 10.1111/dom.13082. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 28786547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Titratable fixed-ratio combination of insulin glargine plus lixisenatide: A simplified approach to glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Dec;170:108478. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108478. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 33002548 Review.
-
[Twice-daily and weekly exenatide: clinical profile of two pioneer formulations in incretin therapy].Med Clin (Barc). 2014 Sep;143 Suppl 2:23-7. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7753(14)70105-8. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Med Clin (Barc). 2014. PMID: 25437462 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Evolving Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Sep-Oct;23(5):351-361. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-23.5.351. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30429688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation of Combination Therapy with Basal Insulin and Either Lixisenatide or Vildagliptin in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Multicenter Study.Diabetes Ther. 2018 Oct;9(5):2067-2079. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0505-2. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Diabetes Ther. 2018. PMID: 30206903 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Sensory and Motor Functions and Energy Intake in Health and Obesity-Therapeutic Implications.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 1;13(4):1158. doi: 10.3390/nu13041158. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33915747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1RAs caused gastrointestinal adverse reactions of drug withdrawal: a system review and network meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 6;14:1149328. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149328. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37484944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monnier L, Colette C, Dunseath GJ, Owens DR. The loss of postprandial glycemic control precedes stepwise deterioration of fasting with worsening diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:263‐269. - PubMed
-
- Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care. 2003;26:881‐885. - PubMed
-
- Peter R, Dunseath G, Luzio SD, Chudleigh R, Choudhury SR, Owens DR. Relative and absolute contributions of postprandial and fasting plasma glucose to daytime hyperglycaemia and HbA(1c) in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2009;26:974‐980. - PubMed
-
- Woerle HJ, Neumann C, Zschau S, et al. Impact of fasting and postprandial glycemia on overall glycemic control in type 2 diabetes importance of postprandial glycemia to achieve target HbA1c levels. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77:280‐285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical