NMR solution structure of the RED subdomain of the Sleeping Beauty transposase
- PMID: 28345263
- PMCID: PMC5441430
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3167
NMR solution structure of the RED subdomain of the Sleeping Beauty transposase
Abstract
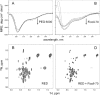
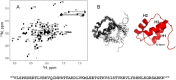
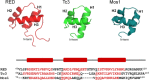
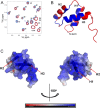
DNA transposons can be employed for stable gene transfer in vertebrates. The Sleeping Beauty (SB) DNA transposon has been recently adapted for human application and is being evaluated in clinical trials, however its molecular mechanism is not clear. SB transposition is catalyzed by the transposase enzyme, which is a multi-domain protein containing the catalytic and the DNA-binding domains. The DNA-binding domain of the SB transposase contains two structurally independent subdomains, PAI and RED. Recently, the structures of the catalytic domain and the PAI subdomain have been determined, however no structural information on the RED subdomain and its interactions with DNA has been available. Here, we used NMR spectroscopy to determine the solution structure of the RED subdomain and characterize its interactions with the transposon DNA.
Keywords: DNA binding; NMR spectroscopy; RED subdomain; SB transposase; folding; structure.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- VandenDriessche T, Ivics Z, Izsvak Z, Chuah MK (2009) Emerging potential of transposons for gene therapy and generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Blood 114:1461–1468. - PubMed
-
- Mates L, Chuah MK, Belay E, Jerchow B, Manoj N, Acosta‐Sanchez A, Grzela DP, Schmitt A, Becker K, Matrai J, Ma L, Samara‐Kuko E, Gysemans C, Pryputniewicz D, Miskey C, Fletcher B, VandenDriessche T, Ivics Z, Izsvak Z (2009) Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive Sleeping Beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat Genet 41:753–761. - PubMed
-
- Narayanavari SA, Chilkunda SS, Ivics Z, Izsvak Z (2017) Sleeping Beauty transposition: from biology to applications. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 52:18–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

