Dapagliflozin once daily plus exenatide once weekly in obese adults without diabetes: Sustained reductions in body weight, glycaemia and blood pressure over 1 year
- PMID: 28345814
- PMCID: PMC5575470
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.12954
Dapagliflozin once daily plus exenatide once weekly in obese adults without diabetes: Sustained reductions in body weight, glycaemia and blood pressure over 1 year
Abstract
Aims: Dapagliflozin and exenatide reduce body weight by differing mechanisms. Dual therapy with these agents reduces body weight, adipose tissue volume, glycaemia and systolic blood pressure (SBP) over 24 weeks. Here, we examined these effects over 1 year in obese adults without diabetes.
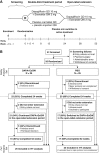
Materials and methods: Obese adults without diabetes (N = 50; aged 18-70 years; body mass index, 30-45 kg/m2 ) were initially randomized to double-blind oral dapagliflozin 10 mg once daily plus subcutaneous long-acting exenatide 2 mg once weekly or to placebo. They entered an open-label extension from 24 to 52 weeks during which all participants received active treatment.
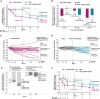
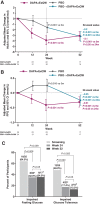
Results: Of the original 25 dapagliflozin + exenatide-treated and 25 placebo-treated participants, respectively, 21 (84%) and 17 (68%) entered the open-label period and 16 (64%) and 17 (68%) completed 52 weeks of treatment. At baseline, mean body weight was 104.6 kg, and 73.5% of participants had prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance). Reductions with dapagliflozin + exenatide at 24 weeks were sustained at 52 weeks, respectively, for body weight (-4.5 and -5.7 kg), total adipose tissue volume (-3.8 and -5.3 L), proportion with prediabetes (34.8% and 35.3%), and SBP (-9.8 and -12.0 mm Hg). Effects on body weight, SBP and glycaemia at 52 weeks with placebo → dapagliflozin + exenatide were similar to those observed with continuation of dapagliflozin + exenatide. Nausea and injection-site reactions were more frequent with dapagliflozin + exenatide than with placebo and diminished over time. Safety and tolerability were similar to that in previous diabetes trials with these agents. No clear difference in adverse event-related withdrawals between placebo and active treatment periods was observed.
Conclusions: Dapagliflozin + exenatide dual therapy produced sustained reductions in body weight, prediabetes and SBP over 52 weeks and was well tolerated in obese adults without diabetes.
Keywords: dapagliflozin; exenatide; obesity; prediabetes.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dapagliflozin once-daily and exenatide once-weekly dual therapy: A 24-week randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study examining effects on body weight and prediabetes in obese adults without diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Jan;19(1):49-60. doi: 10.1111/dom.12779. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27550386 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin once daily versus exenatide or dapagliflozin alone in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy (DURATION-8): a 28 week, multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016 Dec;4(12):1004-1016. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30267-4. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27651331 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of exenatide once weekly plus dapagliflozin, exenatide once weekly, or dapagliflozin, added to metformin monotherapy, on body weight, systolic blood pressure, and triglycerides in patients with type 2 diabetes in the DURATION-8 study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Jun;20(6):1515-1519. doi: 10.1111/dom.13206. Epub 2018 Feb 4. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29316164 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical implications of exenatide as a twice-daily or once-weekly therapy for type 2 diabetes.Postgrad Med. 2011 Sep;123(5):228-38. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.09.2479. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 21904106 Review.
-
[New drugs in type 2 diabetes mellitus therapy].Vnitr Lek. 2013 Aug;59(8):713-8. Vnitr Lek. 2013. PMID: 24007229 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Applications of SGLT2 inhibitors beyond glycaemic control.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Aug;20(8):513-529. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00836-y. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38671190 Review.
-
Effect of exenatide twice daily and dapagliflozin, alone and in combination, on markers of kidney function in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prespecified secondary analysis of a randomized controlled clinical trial.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021 Aug;23(8):1851-1858. doi: 10.1111/dom.14410. Epub 2021 May 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021. PMID: 33908691 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Repurposing Antidiabetic Drugs for Cardiovascular Disease.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 15;11:568632. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.568632. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33041865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of combinations of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes or obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Endocrine. 2020 Feb;67(2):294-304. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-02175-6. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 31900793
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial of Dapagliflozin Plus Once-Weekly Exenatide Versus Placebo in Individuals with Obesity and Without Diabetes: Metabolic Effects and Markers Associated with Bodyweight Loss.Diabetes Ther. 2018 Aug;9(4):1511-1532. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0449-6. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Diabetes Ther. 2018. PMID: 29949016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight: fact sheet no. 311. 2016. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/. Accessed February 2, 2016.
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Altas. 7th ed; 2015. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/. Accessed February 15, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

