EBV induces persistent NF-κB activation and contributes to survival of EBV-positive neoplastic T- or NK-cells
- PMID: 28346502
- PMCID: PMC5367708
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174136
EBV induces persistent NF-κB activation and contributes to survival of EBV-positive neoplastic T- or NK-cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: EBV induces persistent NF-κB activation and contributes to survival of EBV-positive neoplastic T- or NK-cells.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 1;12(8):e0182682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182682. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28763513 Free PMC article.
Abstract
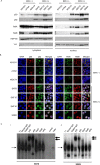
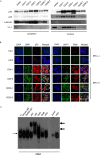
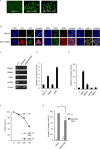
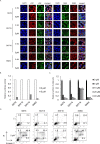
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has been detected in several T- and NK-cell neoplasms such as extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type, aggressive NK-cell leukemia, EBV-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma, systemic EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma of childhood, and chronic active EBV infection (CAEBV). However, how this virus contributes to lymphomagenesis in T or NK cells remains largely unknown. Here, we examined NF-κB activation in EBV-positive T or NK cell lines, SNT8, SNT15, SNT16, SNK6, and primary EBV-positive and clonally proliferating T/NK cells obtained from the peripheral blood of patients with CAEBV. Western blotting, electrophoretic mobility shift assays, and immunofluorescent staining revealed persistent NF-κB activation in EBV-infected cell lines and primary cells from patients. Furthermore, we investigated the role of EBV in infected T cells. We performed an in vitro infection assay using MOLT4 cells infected with EBV. The infection directly induced NF-κB activation, promoted survival, and inhibited etoposide-induced apoptosis in MOLT4 cells. The luciferase assay suggested that LMP1 mediated NF-κB activation in MOLT4 cells. IMD-0354, a specific inhibitor of NF-κB that suppresses NF-κB activation in cell lines, inhibited cell survival and induced apoptosis. These results indicate that EBV induces NF-κB-mediated survival signals in T and NK cells, and therefore, may contribute to the lymphomagenesis of these cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chan JKC, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA, Peh S-C. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type In: Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, editors. WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon IARC Press; 2008. 285–288.
-
- Chan JKC, Jaffe ES, Ralfkiaer E, Ko Y-H. Aggressive NK-cell leukemia In: In: Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, editors. WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon. France: IARC Pre; 2008. 276–277.
-
- Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kimura H, Jaffe ES. EBV-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood In: Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, editors. WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon IARC Press; 2008. 278–280.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

