Cysteine-Functionalized Chitosan Magnetic Nano-Based Particles for the Recovery of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Metals: Uptake Kinetics and Sorption Isotherms
- PMID: 28347004
- PMCID: PMC5312863
- DOI: 10.3390/nano5010154
Cysteine-Functionalized Chitosan Magnetic Nano-Based Particles for the Recovery of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Metals: Uptake Kinetics and Sorption Isotherms
Abstract
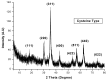
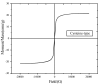
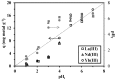
Cysteine-functionalized chitosan magnetic nano-based particles were synthesized for the sorption of light and heavy rare earth (RE) metal ions (La(III), Nd(III) and Yb(III)). The structural, surface, and magnetic properties of nano-sized sorbent were investigated by elemental analysis, FTIR, XRD, TEM and VSM (vibrating sample magnetometry). Experimental data show that the pseudo second-order rate equation fits the kinetic profiles well, while sorption isotherms are described by the Langmuir model. Thermodynamic constants (ΔG°, ΔH°) demonstrate the spontaneous and endothermic nature of sorption. Yb(III) (heavy RE) was selectively sorbed while light RE metal ions La(III) and Nd(III) were concentrated/enriched in the solution. Cationic species RE(III) in aqueous solution can be adsorbed by the combination of chelating and anion-exchange mechanisms. The sorbent can be efficiently regenerated using acidified thiourea.
Keywords: cysteine-grafting; magnetic chitosan nanocomposites; rare earth metals; sorption isotherms; thermodynamics; uptake kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zhang X., Jiao C., Wang J., Liu Q., Li R., Yang P., Zhang M. Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by magnetic schiff base: Kinetic and thermodynamic investigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012;198:412–419. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.090. - DOI
-
- Namdeo M., Bajpai S.K. Chitosan-magnetite nanocomposites (CMNs) as magnetic carrier particles for removal of Fe(III) from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. A. 2008;320:161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.053. - DOI
-
- Hosoba M., Oshita K., Katarina R.K., Takayanagi T., Oshima M., Motomizu S. Synthesis of novel chitosan resin possessing histidine moiety and its application to the determination of trace silver by ICP-AES coupled with triplet automated-pretreatment system. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009;639:51–56. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.02.050. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

