Smart Mesoporous Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy
- PMID: 28347103
- PMCID: PMC5304809
- DOI: 10.3390/nano5041906
Smart Mesoporous Nanomaterials for Antitumor Therapy
Abstract
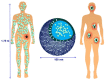
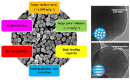
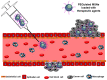
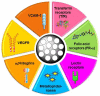
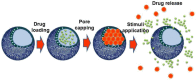
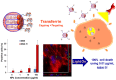
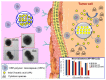
The use of nanomaterials for the treatment of solid tumours is receiving increasing attention by the scientific community. Among them, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) exhibit unique features that make them suitable nanocarriers to host, transport and protect drug molecules until the target is reached. It is possible to incorporate different targeting ligands to the outermost surface of MSNs to selectively drive the drugs to the tumour tissues. To prevent the premature release of the cargo entrapped in the mesopores, it is feasible to cap the pore entrances using stimuli-responsive nanogates. Therefore, upon exposure to internal (pH, enzymes, glutathione, etc.) or external (temperature, light, magnetic field, etc.) stimuli, the pore opening takes place and the release of the entrapped cargo occurs. These smart MSNs are capable of selectively reaching and accumulating at the target tissue and releasing the entrapped drug in a specific and controlled fashion, constituting a promising alternative to conventional chemotherapy, which is typically associated with undesired side effects. In this review, we overview the recent advances reported by the scientific community in developing MSNs for antitumor therapy. We highlight the possibility to design multifunctional nanosystems using different therapeutic approaches aimed at increasing the efficacy of the antitumor treatment.
Keywords: active targeting; cancer treatment; mesoporous silica nanoparticles; passive targeting; stimuli-responsive drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy: our contribution.Biomater Sci. 2016 May 26;4(5):803-13. doi: 10.1039/c6bm00039h. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Biomater Sci. 2016. PMID: 26902682 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the design of smart delivery nanodevices.Biomater Sci. 2013 Feb 3;1(2):114-134. doi: 10.1039/c2bm00085g. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biomater Sci. 2013. PMID: 32481793
-
Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):319-37. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.953051. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25421898 Review.
-
A Review on Recent Technologies and Patents on Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020;14(2):126-144. doi: 10.2174/1872211314666200914155051. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020. PMID: 32928094 Review.
-
Near-infrared light triggered drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles.J Mater Chem B. 2018 Nov 28;6(44):7112-7121. doi: 10.1039/c8tb01548a. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Mater Chem B. 2018. PMID: 32254627
Cited by
-
Covalent Organic Frameworks: From Materials Design to Biomedical Application.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Dec 28;8(1):15. doi: 10.3390/nano8010015. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29283423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery: an update.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Apr;16(4):415-439. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1598375. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30897978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jun 8;12(6):527. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12060527. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32521802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Agents for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 24;13(2):152. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020152. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33498885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZnO Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostic Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Apr 23;8(4):268. doi: 10.3390/nano8040268. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29690644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xia Y., Yang P., Sun Y., Wu Y., Mayers B., Gates B., Yin Y., Kim F., Yan H. One-dimensional nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2003;15:353–389. doi: 10.1002/adma.200390087. - DOI
-
- Vallet-Regí M., Arcos D. Nanoceramics in Clinical Use: From Materials to Applications. 2nd ed. Royal Society of Chemistry; Cambridge, UK: 2015.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

