Magnetic Nanoparticles Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier: When Physics Rises to a Challenge
- PMID: 28347118
- PMCID: PMC5304810
- DOI: 10.3390/nano5042231
Magnetic Nanoparticles Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier: When Physics Rises to a Challenge
Abstract
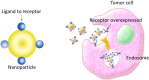
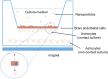
The blood-brain barrier is a physical and physiological barrier that protects the brain from toxic substances within the bloodstream and helps maintain brain homeostasis. It also represents the main obstacle in the treatment of many diseases of the central nervous system. Among the different approaches employed to overcome this barrier, the use of nanoparticles as a tool to enhance delivery of therapeutic molecules to the brain is particularly promising. There is special interest in the use of magnetic nanoparticles, as their physical characteristics endow them with additional potentially useful properties. Following systemic administration, a magnetic field applied externally can mediate the capacity of magnetic nanoparticles to permeate the blood-brain barrier. Meanwhile, thermal energy released by magnetic nanoparticles under the influence of radiofrequency radiation can modulate blood-brain barrier integrity, increasing its permeability. In this review, we present the strategies that use magnetic nanoparticles, specifically iron oxide nanoparticles, to enhance drug delivery to the brain.
Keywords: IONs; blood-brain barrier; magnetic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Strategies to overcome the barrier: use of nanoparticles as carriers and modulators of barrier properties.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Mar;355(3):717-26. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1819-7. Epub 2014 Mar 2. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 24585360 Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Combinational Strategies for Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier and Blood-Tumor Barrier.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 13;19:2529-2552. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S450853. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38505170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation of magnetic nanoparticles crossing through a simplified blood-brain barrier model for Glioblastoma multiforme treatment.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Nov;212:106477. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106477. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34736172
-
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for brain imaging and drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023 Jun;197:114822. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114822. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023. PMID: 37086918 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114485. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114485. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35970274 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Intranasally Delivered Sulforaphane-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Against Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity.Neurotox Res. 2022 Oct;40(5):1479-1498. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00555-x. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35969308 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic exposure to a single dose of ferucarbotran aggravates neuroinflammation in a murine model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Feb 15;14:1229-1240. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S189327. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30863056 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Therapy Using Epitope-Imprinted Composite Nanoparticles to Remove α-Synuclein from an In Vitro Model.Cells. 2022 Aug 19;11(16):2584. doi: 10.3390/cells11162584. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010659 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic modulation of blood-brain barrier permeability to enhance drug delivery.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Dec;18(12):1601-1609. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now137. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27407134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Nanomaterials: The Challenges and Opportunities for Nanomedicines.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jan 8;16:161-184. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S288236. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33447033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

