Polymerization-Incompetent Uromodulin in the Pregnant Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat
- PMID: 28348009
- PMCID: PMC5389592
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08826
Polymerization-Incompetent Uromodulin in the Pregnant Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat
Abstract
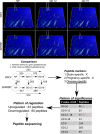
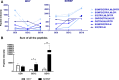
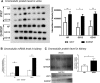
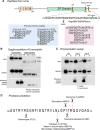
The kidney is centrally involved in blood pressure regulation and undergoes extensive changes during pregnancy. Hypertension during pregnancy may result in an altered urinary peptidome that could be used to indicate new targets of therapeutic or diagnostic interest. The stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHRSP) is a model of maternal chronic hypertension. Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry was conducted to interrogate the urinary peptidome in SHRSP and the control Wistar-Kyoto strain at three time points: prepregnancy and gestational days 12 and 18. The comparison within and between the Wistar-Kyoto and SHRSP peptidome at all time points detected 123 differentially expressed peptides (fold change >1.5; P<0.05). Sequencing of these peptides identified fragments of collagen α-chains, albumin, prothrombin, actin, serpin A3K, proepidermal growth factor, and uromodulin. Uromodulin peptides showed a pregnancy-specific alteration in SHRSP with a 7.8-fold (P<0.01) and 8.8-fold (P<0.05) increase at gestational days 12 and 18, respectively, relative to the Wistar-Kyoto. Further investigation revealed that these peptides belonged to the polymerization-inhibitory region of uromodulin. Two forms of uromodulin (polymerization competent and polymerization incompetent) were found in urine from both Wistar-Kyoto and SHRSP, where the polymerization-incompetent form was increased in a pregnancy-specific manner in SHRSP. Nifedipine-treated pregnant SHRSP showed only polymerization-competent uromodulin, indicating that calcium may be mechanistically involved in uromodulin polymerization. This study highlights, for the first time, a potential role of uromodulin and its polymerization in hypertensive pregnancy.
Keywords: Nifedipine; hypertension; kidney; pregnancy; uromodulin.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pregnancy-associated changes in urinary uromodulin excretion in chronic hypertension.J Nephrol. 2024 Apr;37(3):597-610. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01830-6. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38236469 Free PMC article.
-
Salt loading decreases urinary excretion and increases intracellular accumulation of uromodulin in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Dec 22;135(24):2749-2761. doi: 10.1042/CS20211017. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34870708 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal uterine artery remodelling in the stroke prone spontaneously hypertensive rat.Placenta. 2016 Jan;37:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.10.022. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Placenta. 2016. PMID: 26612342 Free PMC article.
-
Does the kidney play a role in the aetiology of primary hypertension? Evidence from renal transplantation studies in rats and humans.J Hum Hypertens. 1993 Apr;7(2):177-80. J Hum Hypertens. 1993. PMID: 8510091 Review.
-
Pathological alterations of astrocytes in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats under ischemic conditions.Neurochem Int. 2012 Jan;60(1):91-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 22100568 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving Concepts in Uromodulin Biology, Physiology, and Its Role in Disease: a Tale of Two Forms.Hypertension. 2022 Nov;79(11):2409-2418. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.18567. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 35959659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptidomic Analysis of Urine from Youths with Early Type 1 Diabetes Reveals Novel Bioactivity of Uromodulin Peptides In Vitro.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Mar;19(3):501-517. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001858. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31879271 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy-associated changes in urinary uromodulin excretion in chronic hypertension.J Nephrol. 2024 Apr;37(3):597-610. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01830-6. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38236469 Free PMC article.
-
Uromodulin in mineral metabolism.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019 Sep;28(5):481-489. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000522. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31205055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in uromodulin biology and potential clinical applications.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Dec;20(12):806-821. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00881-7. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39160319 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seely EW, Ecker J. Chronic hypertension in pregnancy. Circulation. 2014;129:1254–1261. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003904. - PubMed
-
- Jones DC, Hayslett JP. Outcome of pregnancy in women with moderate or severe renal insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:226–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199607253350402. - PubMed
-
- Imbasciati E, Gregorini G, Cabiddu G, Gammaro L, Ambroso G, Del Giudice A, Ravani P. Pregnancy in CKD stages 3 to 5: fetal and maternal outcomes. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:753–762. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.03.022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

