Long-Term Endothelin-A Receptor Antagonism Provides Robust Renal Protection in Humanized Sickle Cell Disease Mice
- PMID: 28348063
- PMCID: PMC5533228
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016070711
Long-Term Endothelin-A Receptor Antagonism Provides Robust Renal Protection in Humanized Sickle Cell Disease Mice
Abstract
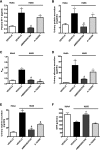
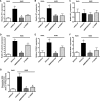
Sickle cell disease (SCD)-associated nephropathy is a major source of morbidity and mortality in patients because of the lack of efficacious treatments targeting renal manifestations of the disease. Here, we describe a long-term treatment strategy with the selective endothelin-A receptor (ETA) antagonist, ambrisentan, designed to interfere with the development of nephropathy in a humanized mouse model of SCD. Ambrisentan preserved GFR at the level of nondisease controls and prevented the development of proteinuria, albuminuria, and nephrinuria. Microscopy studies demonstrated prevention of podocyte loss and structural alterations, the absence of vascular congestion, and attenuation of glomerulosclerosis in treated mice. Studies in isolated glomeruli showed that treatment reduced inflammation and oxidative stress. At the level of renal tubules, ambrisentan treatment prevented the increased excretion of urinary tubular injury biomarkers. Additionally, the treatment strategy prevented tubular brush border loss, diminished tubular iron deposition, blocked the development of interstitial fibrosis, and prevented immune cell infiltration. Furthermore, the prevention of albuminuria in treated mice was associated with preservation of cortical megalin expression. In a separate series of identical experiments, combined ETA and ETB receptor antagonism provided only some of the protection observed with ambrisentan, highlighting the importance of exclusively targeting the ETA receptor in SCD. Our results demonstrate that ambrisentan treatment provides robust protection from diverse renal pathologies in SCD mice, and suggest that long-term ETA receptor antagonism may provide a strategy for the prevention of renal complications of SCD.
Keywords: endothelin; glomerular filtration barrier; proteinuria; renal injury; sickle nephropathy.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures





Comment in
-
Endothelin-A Receptor Antagonism Retards the Progression of Murine Sickle Cell Nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Aug;28(8):2253-2255. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017030320. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28442492 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hassell KL: Population estimates of sickle cell disease in the U.S. Am J Prev Med 38[Suppl]: S512–S521, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Yawn BP, Buchanan GR, Afenyi-Annan AN, Ballas SK, Hassell KL, James AH, Jordan L, Lanzkron SM, Lottenberg R, Savage WJ, Tanabe PJ, Ware RE, Murad MH, Goldsmith JC, Ortiz E, Fulwood R, Horton A, John-Sowah J: Management of sickle cell disease: Summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members. JAMA 312: 1033–1048, 2014 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

