Computational and structural evidence for neurotransmitter-mediated modulation of the oligomeric states of human insulin in storage granules
- PMID: 28348075
- PMCID: PMC5437240
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.775924
Computational and structural evidence for neurotransmitter-mediated modulation of the oligomeric states of human insulin in storage granules
Abstract
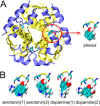
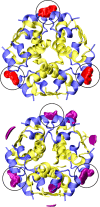
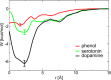
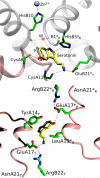
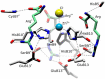
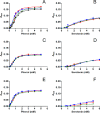
Human insulin is a pivotal protein hormone controlling metabolism, growth, and aging and whose malfunctioning underlies diabetes, some cancers, and neurodegeneration. Despite its central position in human physiology, the in vivo oligomeric state and conformation of insulin in its storage granules in the pancreas are not known. In contrast, many in vitro structures of hexamers of this hormone are available and fall into three conformational states: T6, T3Rf3, and R6 As there is strong evidence for accumulation of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, in insulin storage granules in pancreatic β-cells, we probed by molecular dynamics (MD) and protein crystallography (PC) if these endogenous ligands affect and stabilize insulin oligomers. Parallel studies independently converged on the observation that serotonin binds well within the insulin hexamer (site I), stabilizing it in the T3R3 conformation. Both methods indicated serotonin binding on the hexamer surface (site III) as well. MD, but not PC, indicated that dopamine was also a good site III ligand. Some of the PC studies also included arginine, which may be abundant in insulin granules upon processing of pro-insulin, and stable T3R3 hexamers loaded with both serotonin and arginine were obtained. The MD and PC results were supported further by in solution spectroscopic studies with R-state-specific chromophore. Our results indicate that the T3R3 oligomer is a plausible insulin pancreatic storage form, resulting from its complex interplay with neurotransmitters, and pro-insulin processing products. These findings may have implications for clinical insulin formulations.
Keywords: crystal structure; dopamine; insulin; pancreatic islet; serotonin; vesicles.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of stabilization of the insulin hexamer through allosteric ligand interactions.Biochemistry. 1997 May 13;36(19):5837-45. doi: 10.1021/bi963038q. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9153424
-
Can Arginine Inhibit Insulin Aggregation? A Combined Protein Crystallography, Capillary Electrophoresis, and Molecular Simulation Study.J Phys Chem B. 2018 Nov 8;122(44):10069-10076. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b06557. Epub 2018 Sep 10. J Phys Chem B. 2018. PMID: 30153414
-
Structural asymmetry and half-site reactivity in the T to R allosteric transition of the insulin hexamer.Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 8;33(44):13057-69. doi: 10.1021/bi00248a015. Biochemistry. 1994. PMID: 7947711
-
Zinc-ligand interactions modulate assembly and stability of the insulin hexamer -- a review.Biometals. 2005 Aug;18(4):295-303. doi: 10.1007/s10534-005-3685-y. Biometals. 2005. PMID: 16158220 Review.
-
Biogenesis of the Insulin Secretory Granule in Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1134:17-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12668-1_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30919330 Review.
Cited by
-
The Possible Role of the Type I Chaperonins in Human Insulin Self-Association.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;12(3):448. doi: 10.3390/life12030448. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330199 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin binding to the analytical antibody sandwich pair OXI-005 and HUI-018: Epitope mapping and binding properties.Protein Sci. 2021 Feb;30(2):485-496. doi: 10.1002/pro.4009. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33277949 Free PMC article.
-
A novel optical tracer for VMAT2 applied to live cell measurements of vesicle maturation in cultured human β-cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 1;9(1):5403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41891-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30932004 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance exercise stress: theoretical mechanisms for growth hormone processing and release from the anterior pituitary somatotroph.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023 Sep;123(9):1867-1878. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05263-8. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37421488 Review.
-
A role for foregut tyrosine metabolism in glucose tolerance.Mol Metab. 2019 May;23:37-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30876866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taniguchi C. M., Emanuelli B., and Kahn C. R. (2006) Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 85–96 - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. (2006) Timeline: the twentieth century struggle to decipher insulin signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 867–873 - PubMed
-
- Taylor S. I., Accili D., and Imai Y. (1994) Insulin resistance or insulin deficiency: which is the primary cause of Niddm. Diabetes 43, 735–740 - PubMed
-
- Turner R. C., Hattersley A. T., Shaw J. T., and Levy J. C. (1995) Type-II Diabetes: clinical aspects of molecular biological studies. Diabetes 44, 1–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

