Delineating distinct heme-scavenging and -binding functions of domains in MF6p/helminth defense molecule (HDM) proteins from parasitic flatworms
- PMID: 28348084
- PMCID: PMC5448095
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.771675
Delineating distinct heme-scavenging and -binding functions of domains in MF6p/helminth defense molecule (HDM) proteins from parasitic flatworms
Abstract
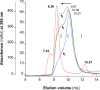
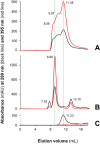
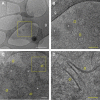
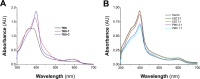
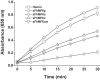
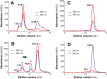
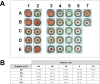
MF6p/FhHDM-1 is a small protein secreted by the parasitic flatworm (trematode) Fasciola hepatica that belongs to a broad family of heme-binding proteins (MF6p/helminth defense molecules (HDMs)). MF6p/HDMs are of interest for understanding heme homeostasis in trematodes and as potential targets for the development of new flukicides. Moreover, interest in these molecules has also increased because of their immunomodulatory properties. Here we have extended our previous findings on the mechanism of MF6p/HDM-heme interactions and mapped the protein regions required for heme binding and for other biological functions. Our data revealed that MF6p/FhHDM-1 forms high-molecular-weight complexes when associated with heme and that these complexes are reorganized by a stacking procedure to form fibril-like and granular nanostructures. Furthermore, we showed that MF6p/FhHDM-1 is a transitory heme-binding protein as protein·heme complexes can be disrupted by contact with an apoprotein (e.g. apomyoglobin) with higher affinity for heme. We also demonstrated that (i) the heme-binding region is located in the MF6p/FhHDM-1 C-terminal moiety, which also inhibits the peroxidase-like activity of heme, and (ii) MF6p/HDMs from other trematodes, such as Opisthorchis viverrini and Paragonimus westermani, also bind heme. Finally, we observed that the N-terminal, but not the C-terminal, moiety of MF6p/HDMs has a predicted structural analogy with cell-penetrating peptides and that both the entire protein and the peptide corresponding to the N-terminal moiety of MF6p/FhHDM-1 interact in vitro with cell membranes in hemin-preconditioned erythrocytes. Our findings suggest that MF6p/HDMs can transport heme in trematodes and thereby shield the parasite from the harmful effects of heme.
Keywords: Fasciola; MF6p/FhHDM-1; MF6p/HDM; cell-penetrating peptide (CPP); fluke; heme; homeostasis; oligomerization; parasite; trematode.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures






References
-
- Ashrafi K., Bargues M. D., O'Neill S., and Mas-Coma S. (2014) Fascioliasis: a worldwide parasitic disease of importance in travel medicine. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 12, 636–649 - PubMed
-
- Haçarız O., Sayers G., and Baykal A. T. (2012) A proteomic approach to investigate the distribution and abundance of surface and internal Fasciola hepatica proteins during the chronic stage of natural liver fluke infection in cattle. J. Proteome Res. 11, 3592–3604 - PubMed
-
- Mulvenna J., Sripa B., Brindley P. J., Gorman J., Jones M. K., Colgrave M. L., Jones A., Nawaratna S., Laha T., Suttiprapa S., Smout M. J., and Loukas A. (2010) The secreted and surface proteomes of the adult stage of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini. Proteomics 10, 1063–1078 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao X., Fu Z., Zhang M., Han Y., Han Q., Lu K., Li H., Zhu C., Hong Y., and Lin J. (2016) Excretory/secretory proteome of 14-day schistosomula, Schistosoma japonicum. J. Proteomics 130, 221–230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

