Myosin-1E interacts with FAK proline-rich region 1 to induce fibronectin-type matrix
- PMID: 28348210
- PMCID: PMC5393228
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1614894114
Myosin-1E interacts with FAK proline-rich region 1 to induce fibronectin-type matrix
Abstract
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase involved in development and human disease, including cancer. It is currently thought that the four-point one, ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM)-kinase domain linker, which contains autophosphorylation site tyrosine (Y) 397, is not required for in vivo FAK function until late midgestation. Here, we directly tested this hypothesis by generating mice with FAK Y397-to-phenylalanine (F) mutations in the germline. We found that Y397F embryos exhibited reduced mesodermal fibronectin (FN) and osteopontin expression and died during mesoderm development akin to FAK kinase-dead mice. We identified myosin-1E (MYO1E), an actin-dependent molecular motor, to interact directly with the FAK FERM-kinase linker and induce FAK kinase activity and Y397 phosphorylation. Active FAK in turn accumulated in the nucleus where it led to the expression of osteopontin and other FN-type matrix in both mouse embryonic fibroblasts and human melanoma. Our data support a model in which FAK Y397 autophosphorylation is required for FAK function in vivo and is positively regulated by MYO1E.
Keywords: cancer; fibronectin; focal adhesion; melanoma; myosin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




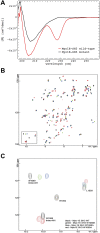

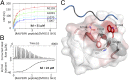



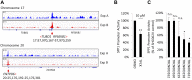

References
-
- Ilić D, et al. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature. 1995;377:539–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

