Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Cadmium from Aqueous Solution by Modified Biomass Ash
- PMID: 28348509
- PMCID: PMC5350408
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3695604
Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Cadmium from Aqueous Solution by Modified Biomass Ash
Abstract
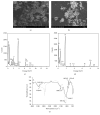
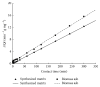
Natural biomass ash of agricultural residuals was collected from a power plant and modified with hexagonal mesoporous silica and functionalized with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. The physicochemical and morphological properties of the biomass ash were analyzed by ICP-OES, SEM, TEM-EDS, FTIR, and BET analysis. The adsorption behavior of the modified product for Cd2+ in aqueous solution was studied as a function of pH, initial metal concentration, equilibrium time, and temperature. Results showed that the specific surface area of the modified product was 9 times that of the natural biomass ash. The modified biomass ash exhibited high affinity for Cd2+ and its adsorption capacity increased sharply with increasing pH from 4.0 to 6.0. The maximum adsorption capacity was 23.95 mg/g in a pH 5 solution with an initial metal concentration of 50 mg/L and a contact time of 90 min. The adsorption of Cd2+ onto the modified biomass ash was well fitted to the Langmuir model and it followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. Thermodynamic analysis results showed that the adsorption of Cd2+ was spontaneous and endothermic in nature. The results suggest that the modified biomass ash is promising for use as an inexpensive and effective adsorbent for Cd2+ removal from aqueous solution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in the manuscript. The authors declare that the grant, scholarship, and funding do not lead to any conflict of interests. Additionally, the authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Removal of Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution Using Biomass Ash and Its Modified Product as Biosorbent.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 24;19(15):9006. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159006. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35897377 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorption of Cu2+ to biomass ash and its modified product.Water Sci Technol. 2017 Apr;2017(1):115-125. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.095. Water Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 29698227
-
[Adsorption of Cd2+ from wastewater by modified fly ash].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2019 Sep;30(9):3215-3223. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201909.040. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31529897 Chinese.
-
Study of the kinetics and the adsorption isotherm of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution using green algae (Ulva lactuca) biomass.Water Sci Technol. 2015;72(9):1505-15. doi: 10.2166/wst.2015.359. Water Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26524441
-
Data on cadmium removal from synthetic aqueous solution using garbage ash.Data Brief. 2018 Sep 1;20:1115-1123. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.08.163. eCollection 2018 Oct. Data Brief. 2018. PMID: 30229127 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Detailed Componential Characterization of Extractable Species with Organic Solvents from Wheat Straw.Int J Anal Chem. 2017;2017:7305682. doi: 10.1155/2017/7305682. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Int J Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 29209369 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorption of nickel and cadmium using Pachira aquatica Aubl. peel biochar.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 1;14(1):5086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54442-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38429371 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of Lead by Merlinoite Prepared from Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Kaolin: Synthesis, Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies.Molecules. 2021 Dec 13;26(24):7550. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247550. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946634 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of clay brick waste for the removal of copper, nickel and iron from aqueous solution: batch and fixed - bed column studies.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 16;8(7):e09963. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09963. eCollection 2022 Jul. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35874057 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution Using Biomass Ash and Its Modified Product as Biosorbent.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 24;19(15):9006. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159006. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35897377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan A. A., de Jong W., Jansens P. J., Spliethoff H. Biomass combustion in fluidized bed boilers: potential problems and remedies. Fuel Processing Technology. 2009;90(1):21–50. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2008.07.012. - DOI
-
- Lei W., Zhuobao D., Zhongxuan W. Experimental study on the adsorption of mercury with modification treatment rice husk ashes and scanning electron microscope analysis. Guangdong Chemical Industry. 2011;38:33–35.
-
- Li X., Xie Y., Yangyang Study on adsorption capacity and kinetic characteristics of plant ash for Cd2+ in sewage water. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University. 2013;44:39–42.
-
- Rautaray S. K., Ghosh B. C., Mittra B. N. Effect of fly ash, organic wastes and chemical fertilizers on yield, nutrient uptake, heavy metal content and residual fertility in a rice–mustard cropping sequence under acid lateritic soils. Bioresource Technology. 2003;90(3):275–283. doi: 10.1016/s0960-8524(03)00132-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

