Tuning Up the Old Brain with New Tricks: Attention Training via Neurofeedback
- PMID: 28348527
- PMCID: PMC5346575
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00052
Tuning Up the Old Brain with New Tricks: Attention Training via Neurofeedback
Abstract
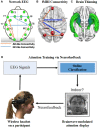
Neurofeedback (NF) is a form of biofeedback that uses real-time (RT) modulation of brain activity to enhance brain function and behavioral performance. Recent advances in Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) and cognitive training (CT) have provided new tools and evidence that NF improves cognitive functions, such as attention and working memory (WM), beyond what is provided by traditional CT. More published studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NF, particularly for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children. In contrast, there have been fewer studies done in older adults with or without cognitive impairment, with some notable exceptions. The focus of this review is to summarize current success in RT NF training of older brains aiming to match those of younger brains during attention/WM tasks. We also outline potential future advances in RT brainwave-based NF for improving attention training in older populations. The rapid growth in wireless recording of brain activity, machine learning classification and brain network analysis provides new tools for combating cognitive decline and brain aging in older adults. We optimistically conclude that NF, combined with new neuro-markers (event-related potentials and connectivity) and traditional features, promises to provide new hope for brain and CT in the growing older population.
Keywords: BCI; EEG; ERP; SVM; biofeedback; brain modulation; cognitive aging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sharpening Working Memory With Real-Time Electrophysiological Brain Signals: Which Neurofeedback Paradigms Work?Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 28;14:780817. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.780817. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35418848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EEG Neurofeedback Training in Children With Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cognitive and Behavioral Outcome Study.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019 Jul;50(4):242-255. doi: 10.1177/1550059418813034. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30453757
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating the Effects of Neurofeedback, Methylphenidate, and Physical Activity on Event-Related Potentials in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2016 May;26(4):344-53. doi: 10.1089/cap.2015.0144. Epub 2016 Jan 15. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26771913 Clinical Trial.
-
SMR Neurofeedback Training Facilitates Working Memory Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Behavioral and EEG Study.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Dec 20;12:321. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00321. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618671 Free PMC article.
-
Using Recent BCI Literature to Deepen our Understanding of Clinical Neurofeedback: A Short Review.Neuroscience. 2018 May 15;378:225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29572165 Review.
Cited by
-
Sharpening Working Memory With Real-Time Electrophysiological Brain Signals: Which Neurofeedback Paradigms Work?Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 28;14:780817. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.780817. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35418848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poststroke Cognitive Impairment Research Progress on Application of Brain-Computer Interface.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Feb 7;2022:9935192. doi: 10.1155/2022/9935192. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35252458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gauging Working Memory Capacity From Differential Resting Brain Oscillations in Older Individuals With A Wearable Device.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 19;13:625006. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.625006. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716711 Free PMC article.
-
Network Brain-Computer Interface (nBCI): An Alternative Approach for Cognitive Prosthetics.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 1;12:790. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00790. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30443203 Free PMC article.
-
Human enhancement through the lens of experimental and speculative neurotechnologies.Hum Behav Emerg Technol. 2019 Oct;1(4):361-372. doi: 10.1002/hbe2.179. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Hum Behav Emerg Technol. 2019. PMID: 31894206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abiri R., Heise G., Zhao X., Jiang Y. (2015a). “EEG-based control of a unidimensional computer cursor using imagined body kinematics,” in Paper Presented at the Biomedical Engineering Society Annual Meeting (Tampa, FL).
-
- Abiri R., McBride J., Zhao X., Jiang Y. (2015b). “A real-time brainwave based neuro-feedback system for cognitive enhancement,” in Paper Presented at the ASME 2015 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (Columbus, OH).
-
- Abiri R., Zhao X., Jiang Y. (2016a). “Controlling gestures of a social robot in a brain machine interface platform,” in Paper Presented at the International Brain Computer Interface Meeting (Pacific Grove, CA).
-
- Abiri R., Zhao X., Jiang Y. (2016b). “A real-time EEG-based neurofeedback platform for attention training,” in Paper Presented at the Biomedical Engineering Society Annual Meeting (Minneapolis, MN).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

