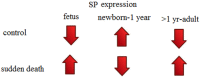
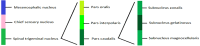Substance P/Neurokinin 1 and Trigeminal System: A Possible Link to the Pathogenesis in Sudden Perinatal Deaths
- PMID: 28348544
- PMCID: PMC5346962
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00082
Substance P/Neurokinin 1 and Trigeminal System: A Possible Link to the Pathogenesis in Sudden Perinatal Deaths
Abstract
Sudden demise of a healthy fetus or a neonate is a very tragic episode in the life of parents. These deaths have been a mystery since ages but still remain unexplained. This review proposes the involvement of trigeminal nerve, neurotransmitter substance P (SP), and its receptor neurokinin 1 (NK-1R) in regulation of cardiorespiratory control in fetuses and newborns. Anomalies and immaturity of neuroregulatory systems such as trigeminal system in medulla oblongata of brainstem may provide a possible mechanism of sudden perinatal deaths. Vulnerable infants are born with respiratory center immaturity which in combination with any stressor such as cold, hypoxia, and smoking may lead to cessation of breathing and ventilatory response. SP/NK-1R may be involved in regulating the ventilatory control in neonates while it is decreased in fetal and adult life in humans, and any alterations from these may lead to irreversible sleep apnea and fatal breathing, ultimately sudden death. This review summarizes the studies performed to highlight the expression of SP or NK-1R in sudden perinatal deaths and proposes the involvement of trigeminal ganglion along with its nerve and SP/NK-1R expression alteration as one of the possible pathophysiological underlying mechanism. However, further studies are required to explore the role of SP, NK-1R, and trigeminal system in the pathogenesis of sudden infant deaths, sudden intrauterine deaths, stillbirths, and sudden deaths later in human life.
Keywords: neurokinin 1 receptor; substance P; sudden infant deaths; sudden perinatal death; trigeminal nerve.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Towards Better Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Neuronal Respiratory Network in Sudden Perinatal Death.Front Neurol. 2017 Jul 6;8:320. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00320. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28729852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormalities in substance P neurokinin-1 receptor binding in key brainstem nuclei in sudden infant death syndrome related to prematurity and sex.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0184958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184958. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931039 Free PMC article.
-
Role of somatostatin and apoptosis in breathing control in sudden perinatal and infant unexplained death.Clin Neuropathol. 2004 Nov-Dec;23(6):304-10. Clin Neuropathol. 2004. PMID: 15584216
-
Developmental alterations of the spinal trigeminal nucleus disclosed by substance P immunohistochemistry in fetal and infant sudden unexplained deaths.Neuropathology. 2011 Aug;31(4):405-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2010.01190.x. Epub 2011 Jan 30. Neuropathology. 2011. PMID: 21276082
-
Neurochemical Alterations in Sudden Unexplained Perinatal Deaths-A Review.Front Pediatr. 2018 Jan 25;6:6. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00006. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29423392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Substance P/ Neurokinin-1 Receptor, Trigeminal Ganglion, Latency, and Coronavirus Infection-Is There Any Link?Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 18;8:727593. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.727593. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34869423 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Neurokinin-1 Receptor Expression Is Associated with Human Dental Pulp Inflammation and Pain Severity.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 5;2021:5593520. doi: 10.1155/2021/5593520. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34041298 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Expression of the Alpha Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor 7 in the Human Normal, Diabetic, and Preeclamptic Placenta and Products of Conception.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 25;11:607239. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.607239. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33324243 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Better Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Neuronal Respiratory Network in Sudden Perinatal Death.Front Neurol. 2017 Jul 6;8:320. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00320. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28729852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormalities in substance P neurokinin-1 receptor binding in key brainstem nuclei in sudden infant death syndrome related to prematurity and sex.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0184958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184958. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergman AB, Beckwith JB, Ray CG. Sudden infant death syndrome. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Causes of Sudden Death in Infants Seattle: University of Washington Press; (1970).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources