A Member of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Brachypodium distachyon, BdGF14d, Confers Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants
- PMID: 28348575
- PMCID: PMC5346558
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00340
A Member of the 14-3-3 Gene Family in Brachypodium distachyon, BdGF14d, Confers Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants
Abstract
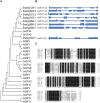
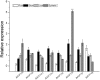
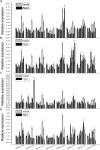
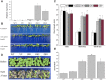
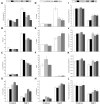
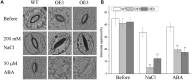
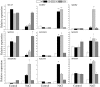
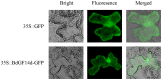
Plant 14-3-3 proteins are involved in diverse biological processes, but for the model monocotyledonous species, Brachypodium distachyon, their roles in abiotic stress tolerance are not well understood. In this study, a total of eight Bd14-3-3 genes were identified from B. distachyon and these were designated respectively as BdGF14a-BdGF14g. The qRT-PCR analyses of 3-month-old plants of B. distachyon showed that these genes were all expressed in the stems, leaves, and spikelets. By contrast, most of the plants had relatively lower transcriptional levels in their roots, except for the BdGF14g gene. The different expression profiles of the Bd14-3-3s under various stress treatments, and the diverse interaction patterns between Bd14-3-3s and BdAREB/ABFs, suggested that these gene products probably had a range of functions in the stress responses. The NaCl-induced Bd14-3-3 gene, BdGF14d, was selected for overexpression in tobacco. BdGF14d was found to be localized throughout the cell and it conferred enhanced tolerance to salt in the transgenic plants. Lowered contents of malondialdehyde, H2O2, and Na+, and lower relative electronic conductance (Rec%), yet greater activities of catalase and peroxidase, were observed in the overexpressing plants. Higher photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, and water use efficiency were measured in the transgenic lines. Following abscisic acid (ABA) or NaCl treatment, stomatal aperture in leaves of the BdGF14d-overexpression plants was significantly lower than in leaves of the wild type (WT) controls. The stress-related marker genes involved in the ABA signaling pathway, the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging system, and the ion transporters were all up-regulated in the BdGF14d-overexpressing plants as compared with WT. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the Bd14-3-3 genes play important roles in abiotic stress tolerance. The ABA signaling pathway, the ROS-scavenging system, and ion transporters were all involved in enhancing the tolerance to salt stress in the BdGF14d-overexpression plants.
Keywords: ABA signaling; B. distachyon; Bd14-3-3s; BdGF14d; ROS-scavenging system; salt tolerance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A 14-3-3 Protein-Encoding Gene, BdGF14g, Confers Better Drought Tolerance by Regulating ABA Biosynthesis and Signaling.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;12(23):3975. doi: 10.3390/plants12233975. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068611 Free PMC article.
-
BdCIPK31, a Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase, Regulates Plant Response to Drought and Salt Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jul 7;8:1184. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01184. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28736568 Free PMC article.
-
The cotton WRKY transcription factor GhWRKY17 functions in drought and salt stress in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana through ABA signaling and the modulation of reactive oxygen species production.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Dec;55(12):2060-76. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu133. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25261532
-
Overexpression of wheat α-mannosidase gene TaMP impairs salt tolerance in transgenic Brachypodium distachyon.Plant Cell Rep. 2020 May;39(5):653-667. doi: 10.1007/s00299-020-02522-2. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Plant Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32123996
-
The 14-3-3 Protein BdGF14a Increases the Transcriptional Regulation Activity of BdbZIP62 to Confer Drought and Salt Resistance in Tobacco.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;13(2):245. doi: 10.3390/plants13020245. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256798 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Wheat 14-3-3 Genes Unravels the Role of TaGRF6-A in Salt Stress Tolerance by Binding MYB Transcription Factor.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 14;22(4):1904. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041904. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33673010 Free PMC article.
-
PpNUDX8, a Peach NUDIX Hydrolase, Plays a Negative Regulator in Response to Drought Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 16;12:831883. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.831883. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35251068 Free PMC article.
-
A 14-3-3 Protein-Encoding Gene, BdGF14g, Confers Better Drought Tolerance by Regulating ABA Biosynthesis and Signaling.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;12(23):3975. doi: 10.3390/plants12233975. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068611 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the 14-3-3 gene family in monocotyledons and dicotyledons and validation of MdGRF13 function in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Aug;42(8):1345-1364. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03035-4. Epub 2023 May 31. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37253815
-
The role of 14-3-3 proteins in plant growth and response to abiotic stress.Plant Cell Rep. 2022 Apr;41(4):833-852. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02803-4. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Plant Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 34773487 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

