Complications after implantation of subcutaneous central venous ports (PowerPortⓇ)
- PMID: 28348733
- PMCID: PMC5358939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.03.014
Complications after implantation of subcutaneous central venous ports (PowerPortⓇ)
Abstract
Background: The aim of our study was revised as follows: to clarify the postoperative complications of multifunctional central venous ports and the risk factors for such complications to promote the safe use of the PowerPort system in the hospital.
Methods: The study group comprised 132 patients in whom implantable central venous access ports (PowerPortⓇ) were placed in our hospital from March 2014 through December 2015. The approach used for port placement was the subclavian vein in 43 patients (33%), the internal jugular vein in 87 patients (66%), and the femoral vein in 2 patients (1%).
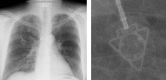
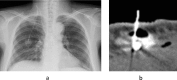
Results: Postoperative complications occurred in 8 patients (6%). The catheter was removed because of infection in 4 patients and catheter kinking in 1 patient. Port extravasation occurred in 3 patients. No patient had catheter pinch-off. The mean operation time was 74 min (range, 32 to 171). No patients had intraoperative bleeding or pneumothorax. Benign disease was a risk factor for postoperative complications (p = 0.009).
Conclusion: PowerPort is a multifunctional port. Benign disease was a risk factor for postoperative complications. Because many types of subcutaneously implanted ports are used in our hospital, we had to inform the hospital staff about the functions of PowerPort.
Keywords: Implantation central venous access port; Multifunctional port; Power port.
Figures

References
-
- Kock H.J., Pietsch M., Krause U. Implantable vascular access systems: experience in 1500 patients with totally implantable central venous port systems. World J. Surg. 1998;22:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Marcy P.Y., Magne N., Castadot P. Radiological and surgical placement of ports devices: a 4-year institutional analysis of procedure performance, quality of life and cost in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treast. 2005;92:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto N., Arai Y., Kakeuchi Y. Ultrasound-guided radiological placement of central venous port via the subclavian vein: a retrospective analysis of 500 cases at a single institute. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010;33:989–994. - PubMed
-
- Vescia S., Baumgratner A.K., Jacobs V.R. Management of venous port systems in oncology: a review of current evidence. Ann. Oncol. 2008;19:9–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

