Capparis spinosa L. aqueous extract evokes antidiabetic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- PMID: 28348974
- PMCID: PMC5355824
Capparis spinosa L. aqueous extract evokes antidiabetic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
Abstract
Objective: As the aqueous extract of Capparis spinosa (CS) possess antidiabetic effect, he present study aims to reveal the possible mechanism of action of CS in diabetic mice.
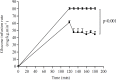
Materials and methods: Both single and repeated oral administrations of aqueous extract of CS were performed in multi-low dose streptozotocin-induced (MLDS) diabetic mice. Euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp was used in association with the endogenous glucose production (perfusion rate of 3-3H glucose) to evaluate the effect of CS aqueous extract on insulin sensitivity.
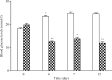
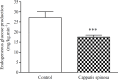
Results: Our study showed that aqueous extract of CS possess a potent hypoglycaemic activity in MLDS diabetic mice. Furthermore, the analysis perfusion of 3-3H glucose demonstrated the parallel decrease of basal endogenous glucose production (EGP) with the hypoglycaemic activity. EGP was lower in CS-Treated group when compared to the control group (p<0.001). The euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique demonstrated that CS treatment improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
Conclusion: We conclude that the antihyperglycemic effet CS is probably due to the inhibition of basal endogenous glucose production and the improvement of insulin sensitivity in MLDS diabetic mice.
Keywords: Diabetes; Insulin sensitivity; Mice; Streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adeneye AA. The leaf and seed aqueousextract of Phyllanthus amarus improvesinsulin resistance diabetes in experimental animal studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;144:705–711. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. [Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus]; Diabetes Care. 2014 37:81–90.
-
- Burcelin R, Eddouks M, Maury J, Kand J, Assan R, Girard J. Excessive glucose production, rather than insulin resistance, accounts for hyperglycaemia in recent-onset streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1995;38:283–290. - PubMed
-
- Chen YI, Cheng YW, Tzeng CY, Lee YC, Chang YN, Lee SC, Tsai CC, Chen JC, Tzen JT, Chang SL. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor activating hypoglycemic effect of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis aqueousextract and improvement of insulin sensitivity in steroid induced insulin resistant rats. BMC Complementar Altern Med. 2014;14:10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eddouks M, Maghrani M, Lemhadri A, Ouahidi ML, Jouad H. Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiac diseases in the south-east region of Morocco (Tafilalet) J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;82:97–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
