The Orexin System and Hypertension
- PMID: 28349223
- PMCID: PMC5617754
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-017-0487-z
The Orexin System and Hypertension
Abstract
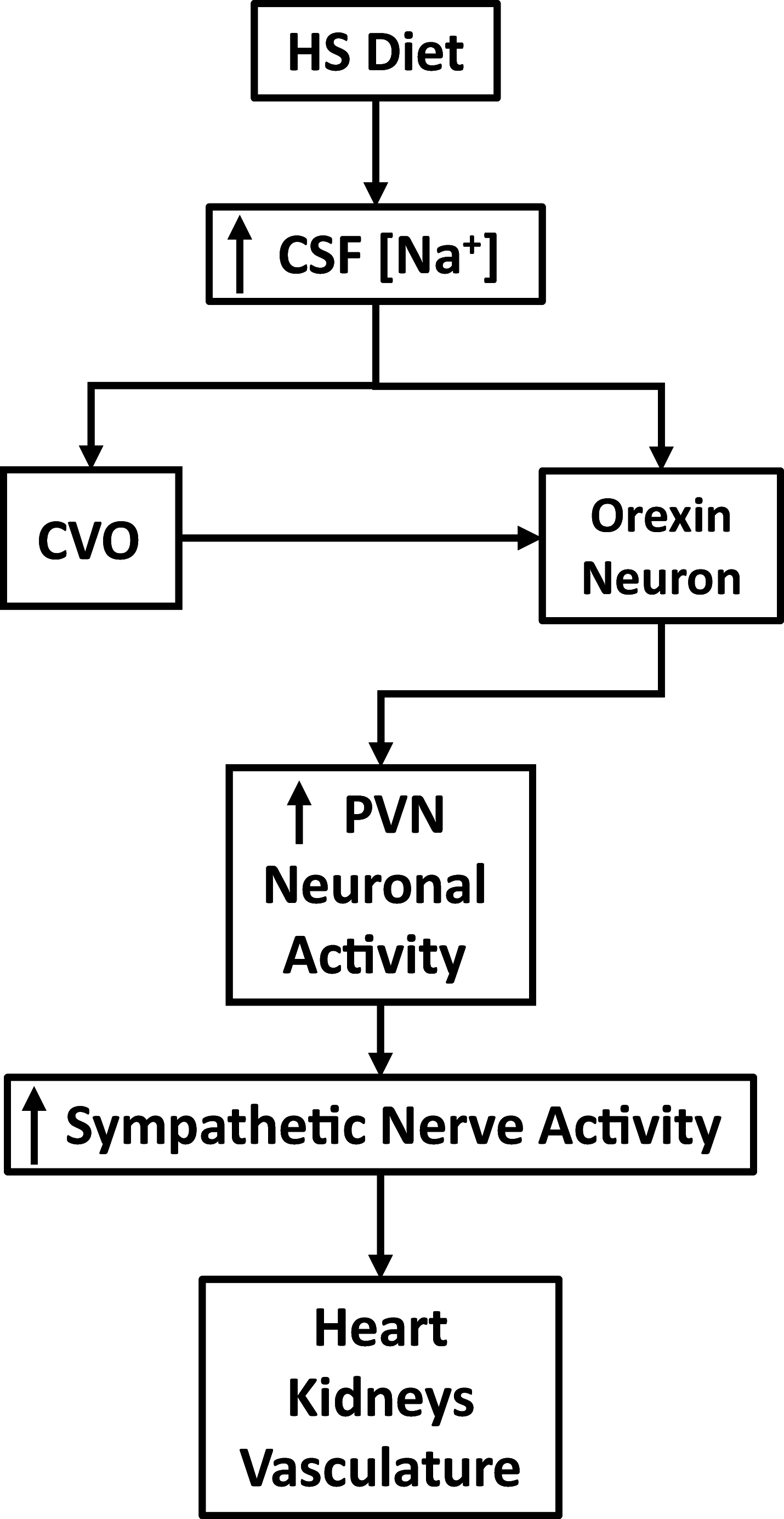
In this review, we focus on the role of orexin signaling in blood pressure control and its potential link to hypertension by summarizing evidence from several experimental animal models of hypertension. Studies using the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) animal model of human essential hypertension show that pharmacological blockade of orexin receptors reduces blood pressure in SHRs but not in Wistar-Kyoto rats. In addition, increased activity of the orexin system contributes to elevated blood pressure and sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) in dark-active period Schlager hypertensive (BPH/2J) mice, another genetic model of neurogenic hypertension. Similar to these two models, Sprague-Dawley rats with stress-induced hypertension display an overactive central orexin system. Furthermore, upregulation of the orexin receptor 1 increases firing of hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons, augments SNA, and contributes to hypertension in the obese Zucker rat, an animal model of obesity-related hypertension. Finally, we propose a hypothesis for the implication of the orexin system in salt-sensitive hypertension. All of this evidence, coupled with the important role of elevated SNA in increasing blood pressure, strongly suggests that hyperactivity of the orexin system contributes to hypertension.
Keywords: Hypertension; Orexin; Salt-sensitive hypertension; Sympathetic nerve activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amin MS, Reza E, Wang H, Leenen FH (2009) Sodium transport in the choroid plexus and salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 54:860–867. doi:10.1161/hypertensionaha.108.125807 - PubMed
-
- Andresen MC, Kuraoka S, Brown AM (1980) Baroreceptor function and changes in strain sensitivity in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res 47:821–828 - PubMed
-
- Antunes VR, Brailoiu GC, Kwok EH, Scruggs P, Dun NJ (2001) Orexins/hypocretins excite rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281:R1801–R1807 - PubMed
-
- Backberg M, Hervieu G, Wilson S, Meister B (2002) Orexin receptor-1 (OX-R1) immunoreactivity in chemically identified neurons of the hypothalamus: focus on orexin targets involved in control of food and water intake. Eur J Neurosci 15:315–328 - PubMed
-
- Baldo BA, Daniel RA, Berridge CW, Kelley AE (2003) Overlapping distributions of orexin/hypocretin- and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase immunoreactive fibers in rat brain regions mediating arousal, motivation, and stress. J Comp Neurol 464:220–237. doi:10.1002/cne.10783 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

