Scholarly concentration programs and medical student research productivity: a systematic review
- PMID: 28349265
- PMCID: PMC5542888
- DOI: 10.1007/s40037-017-0328-2
Scholarly concentration programs and medical student research productivity: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Scholarly concentration programs have become a common method to promote student inquiry and independent research in medical schools. Given the high resource requirements of scholarly concentration program implementation, it is important to examine program efficacy. This systematic review examined the impact of scholarly concentration programs on student research productivity.
Methods: The authors carried out a literature search to find articles related to scholarly concentration program research productivity outcomes. The inclusion criterion was a method of rigorously evaluating program scholarly productivity. Study rigour was evaluated with the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument.
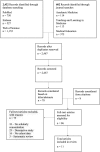
Results: The initial search disclosed 2467 unique records: 78 were considered based on titles and abstracts; eight were considered by scanning references. Eleven papers met the inclusion criteria: all were descriptive; none had a priori hypotheses that examined predictors of medical student research productivity in scholarly concentration programs or prospectively evaluated program impact on student scholarly output.
Discussion: While few in number and often lacking in rigour, the studies included herein suggest that adequate administrative support, strong mentorship and tailored program characteristics are essential in facilitating student research productivity in scholarly concentration programs. Given the challenges inherent in medical education research, a conceptual framework based on United Way's approach may help program planners and educators address this gap in the evaluation of scholarly concentration programs.
Keywords: Program evaluation; Scholarly activity; Scholarly concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
A.G. Havnaer, A.J. Chen and P.B. Greenberg declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
Prior institutional review board approval was not required as this study did not involve human participants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scholarly Concentration Program Development: A Generalizable, Data-Driven Approach.Acad Med. 2016 Nov;91(11 Association of American Medical Colleges Learn Serve Lead: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Research in Medical Education Sessions):S16-S23. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001362. Acad Med. 2016. PMID: 27779505
-
Developing future leaders in reproductive health through a scholarly concentration for medical students.Contraception. 2014 Nov;90(5):508-13. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Contraception. 2014. PMID: 25107640
-
A 5-year experience with an elective scholarly concentrations program.Med Educ Online. 2015 Nov 9;20:29278. doi: 10.3402/meo.v20.29278. eCollection 2015. Med Educ Online. 2015. PMID: 26561482 Free PMC article.
-
A review of literature on medical students and scholarly research: experiences, attitudes, and outcomes.Acad Med. 2015 Aug;90(8):1162-73. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000702. Acad Med. 2015. PMID: 25853690 Review.
-
Facilitating student retention in online graduate nursing education programs: a review of the literature.Nurse Educ Today. 2014 Jul;34(7):1125-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Nurse Educ Today. 2014. PMID: 24529796 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictors of Medical Students' Views toward Research: Insights from a Cross-Cultural Study among Portuguese-Speaking Countries.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;10(2):336. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10020336. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35206950 Free PMC article.
-
Using an Extracurricular Honors Program to Engage Future Physicians Into Scientific Research in Early Stages of Medical Training.Med Sci Educ. 2018;28(2):451-455. doi: 10.1007/s40670-018-0565-y. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Med Sci Educ. 2018. PMID: 31007968 Free PMC article.
-
The association between medical student research engagement with learning outcomes.Med Educ Online. 2022 Dec;27(1):2100039. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2022.2100039. Med Educ Online. 2022. PMID: 35818325 Free PMC article.
-
The association of a scholarly concentrations program with medical students' matched residencies.Med Educ Online. 2023 Dec;28(1):2234651. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2023.2234651. Med Educ Online. 2023. PMID: 37434383 Free PMC article.
-
Portuguese Medical Students' Interest for Science and Research Declines after Freshman Year.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;9(10):1357. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9101357. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34683037 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous