Discriminating cognitive status in Parkinson's disease through functional connectomics and machine learning
- PMID: 28349948
- PMCID: PMC5368610
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45347
Discriminating cognitive status in Parkinson's disease through functional connectomics and machine learning
Abstract
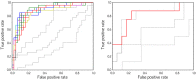
There is growing interest in the potential of neuroimaging to help develop non-invasive biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, connection-wise patterns of functional connectivity were used to distinguish Parkinson's disease patients according to cognitive status using machine learning. Two independent subject samples were assessed with resting-state fMRI. The first (training) sample comprised 38 healthy controls and 70 Parkinson's disease patients (27 with mild cognitive impairment). The second (validation) sample included 25 patients (8 with mild cognitive impairment). The Brainnetome atlas was used to reconstruct the functional connectomes. Using a support vector machine trained on features selected through randomized logistic regression with leave-one-out cross-validation, a mean accuracy of 82.6% (p < 0.002) was achieved in separating patients with mild cognitive impairment from those without it in the training sample. The model trained on the whole training sample achieved an accuracy of 80.0% when used to classify the validation sample (p = 0.006). Correlation analyses showed that the connectivity level in the edges most consistently selected as features was associated with memory and executive function performance in the patient group. Our results demonstrate that connection-wise patterns of functional connectivity may be useful for discriminating Parkinson's disease patients according to the presence of cognitive deficits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aarsland D. et al. Cognitive impairment in incident, untreated Parkinson disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. Neurology 72, 1121–1126 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Muslimovic D., Post B., Speelman J. D. & Schmand B. Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurology 65, 1239–45 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Aarsland D. & Kurz M. W. The epidemiology of dementia associated with Parkinson disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 289, 18–22 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Hely M. A., Reid W. G. J., Adena M. A., Halliday G. M. & Morris J. G. L. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov. Disord. 23, 837–44 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

