Mechanotransduction current is essential for stability of the transducing stereocilia in mammalian auditory hair cells
- PMID: 28350294
- PMCID: PMC5407859
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.24661
Mechanotransduction current is essential for stability of the transducing stereocilia in mammalian auditory hair cells
Abstract
Mechanotransducer channels at the tips of sensory stereocilia of inner ear hair cells are gated by the tension of 'tip links' interconnecting stereocilia. To ensure maximal sensitivity, tip links are tensioned at rest, resulting in a continuous influx of Ca2+ into the cell. Here, we show that this constitutive Ca2+ influx, usually considered as potentially deleterious for hair cells, is in fact essential for stereocilia stability. In the auditory hair cells of young postnatal mice and rats, a reduction in mechanotransducer current, via pharmacological channel blockers or disruption of tip links, leads to stereocilia shape changes and shortening. These effects occur only in stereocilia that harbor mechanotransducer channels, recover upon blocker washout or tip link regeneration and can be replicated by manipulations of extracellular Ca2+ or intracellular Ca2+ buffering. Thus, our data provide the first experimental evidence for the dynamic control of stereocilia morphology by the mechanotransduction current.
Keywords: actin; calcium; cell biology; deafness; hair cells; mechanotransduction; mouse; neuroscience; rat; stereocilia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


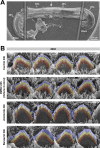





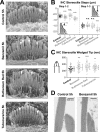
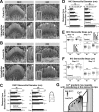

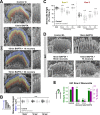

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

