Cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract from Markhamia tomentosa (Benth.) K. Schum. stem bark in a rat model of scopolamine
- PMID: 28351401
- PMCID: PMC5371259
- DOI: 10.1186/s12993-017-0123-6
Cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract from Markhamia tomentosa (Benth.) K. Schum. stem bark in a rat model of scopolamine
Abstract
Background: Plants of the genus Markhamia have been traditionally used by different tribes in various parts of West African countries, including Cameroun. Markhamia tomentosa (Benth.) K. Schum. (Bignoniaceae) is used as an antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant and anti-Alzheimer agent. The current study was undertaken in order to investigate its anti-amnesic and antioxidant potential on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and to determine its possible mechanism of action.
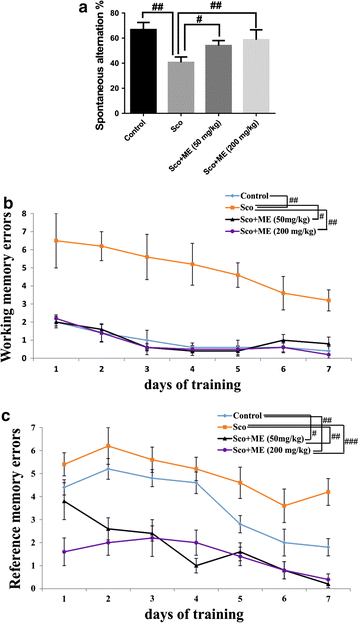
Methods: Rats were pretreated with the aqueous extract (50 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.), for 10 days, and received a single injection of scopolamine (0.7 mg/kg, i.p.) before training in Y-maze and radial arm-maze tests. The biochemical parameters in the rat hippocampus were also assessed to explore oxidative status. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. F values for which p < 0.05 were regarded as statistically significant.
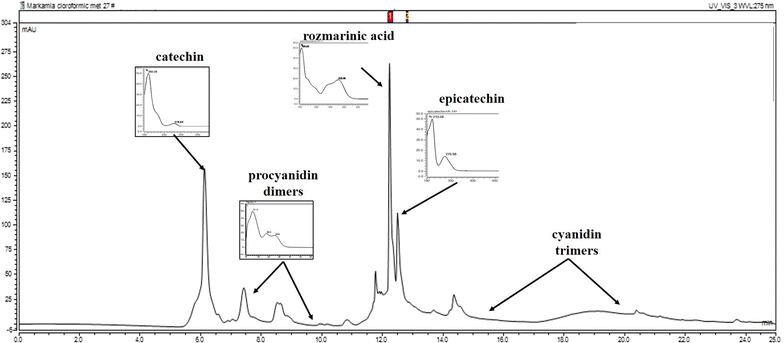
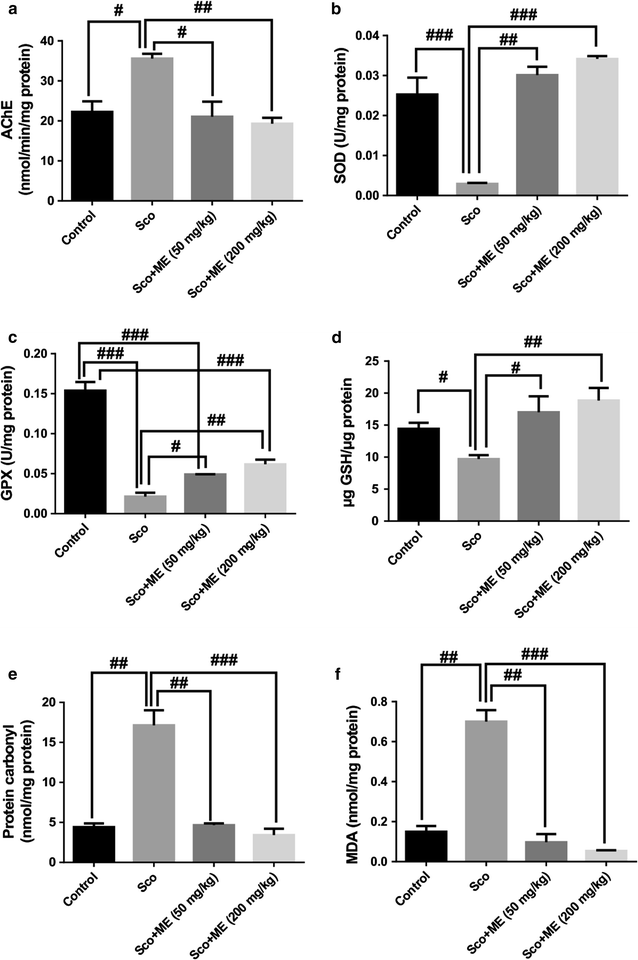
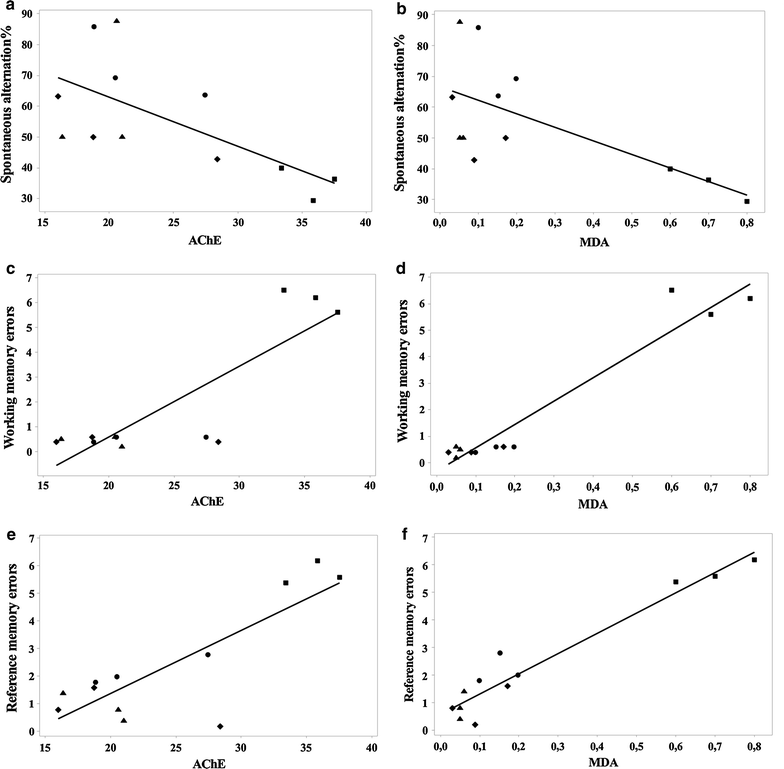
Results: In the scopolamine-treated rats, the aqueous extract improved memory in behavioral tests and decreased the oxidative stress in the rat hippocampus. Also, the aqueous extract exhibited anti-acetylcholinesterase activity.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the aqueous extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment by attenuation of the oxidative stress in the rat hippocampus.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Alzheimer’s disease; Markhamia tomentosa stem bark extract; Oxidative stress; Scopolamine; Spatial memory.
Figures

References
-
- Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Pérez CA, Moreno RD, Vicente M, Linker C, Casanueva OI, Soto C, Garrido J. Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-β-peptides into Alzheimer’s fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of the enzyme. Neuron. 1996;16(4):881–891. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80108-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

