Identification of a novel merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium vivax, PvMSA180
- PMID: 28351409
- PMCID: PMC5369000
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-017-1760-9
Identification of a novel merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium vivax, PvMSA180
Abstract
Background: Although a number of Plasmodium vivax proteins have been identified, few have been investigated as potential vaccine candidates. This study characterized the Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface antigen 180 (PvMSA180, PVX_094920), a novel P. vivax antigenic protein.
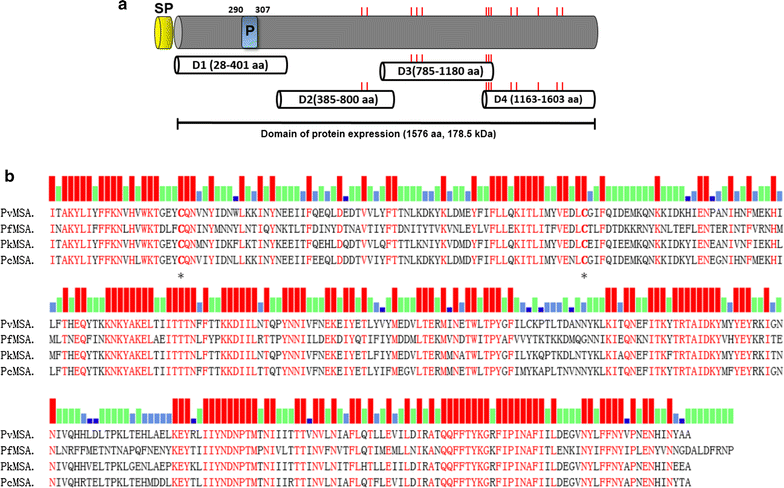
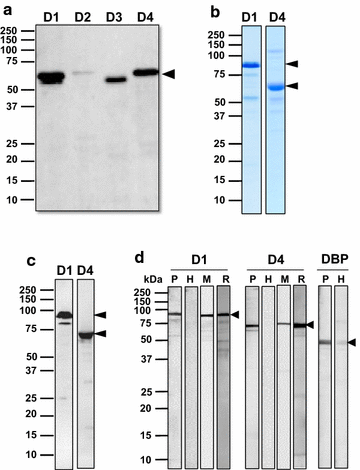
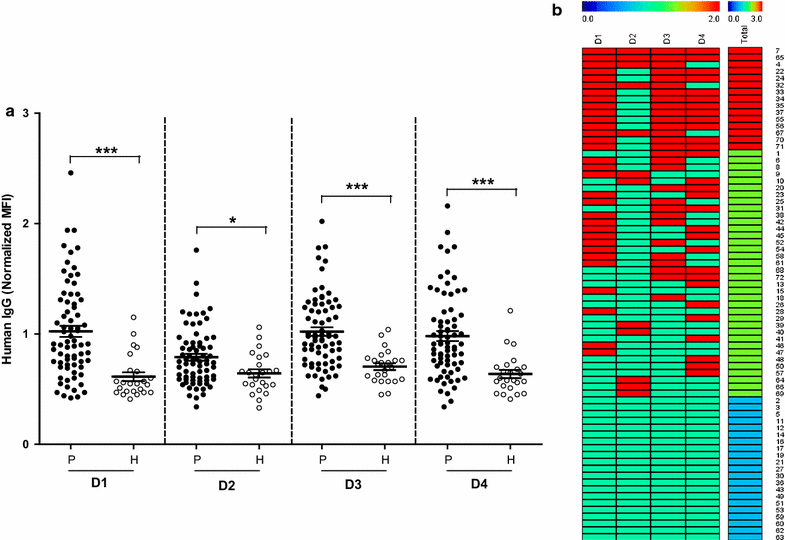
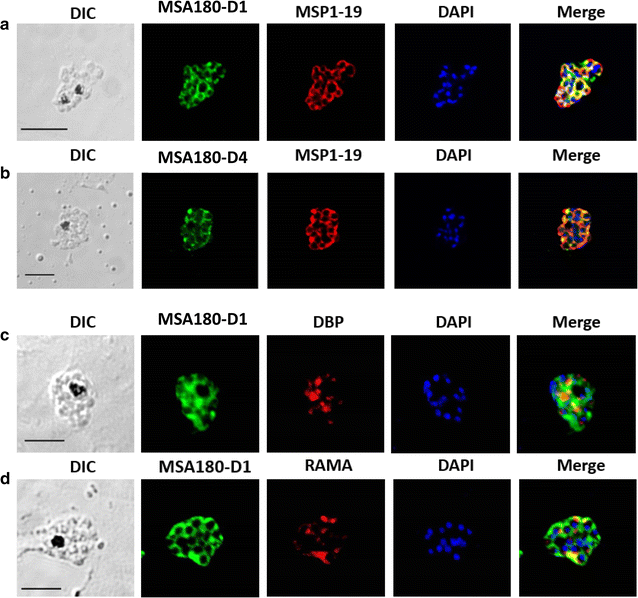
Methods: The target gene was amplified as four overlapping domains (D1, D2, D3 and D4) to enable expression of the recombinant protein using cell-free and bacterial expression systems. The recombinant PvMSA180 proteins were used in protein microarrays to evaluate the humoral immune response of 72 vivax-infected patients and 24 vivax-naïve individuals. Antibodies produced in mice against the PvMSA180-D1 and -D4 domains were used to assess the subcellular localization of schizont-stage parasites with immunofluorescence assays. A total of 51 pvmsa180 sequences from 12 countries (41 sequences from PlasmoDB and 6 generated in this study) were used to determine the genetic diversity and genealogical relationships with DNAsp and NETWORK software packages, respectively.
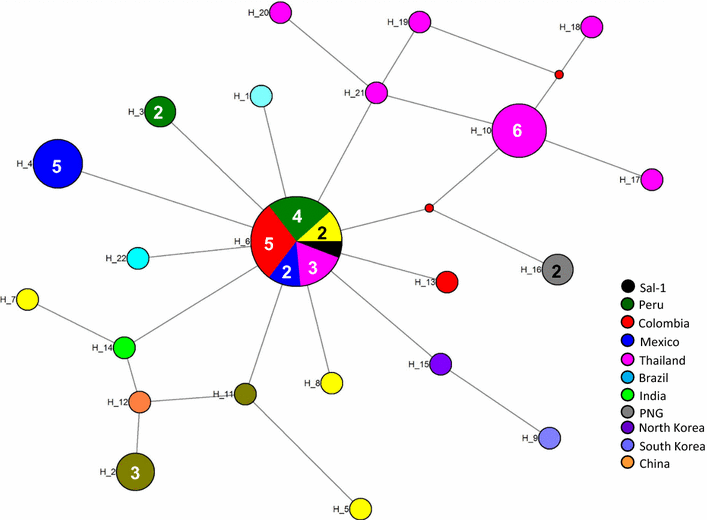
Results: PvMSA180 consists of 1603 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 182 kDa, and has a signal peptide at the amino-terminus. A total of 70.8% of patients (51/72) showed a specific antibody response to at least one of the PvMSA180 domains, and 20.8% (15/72) exhibited a robust antibody response to at least three of the domains. These findings suggest that PvMSA180 is targeted by the humoral immune response during natural infection with P. vivax. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that PvMSA180 is localized on the merozoite surface of schizont-stage parasites, and pvmsa180 sequences originating from various geographic regions worldwide showed low genetic diversity. Twenty-two haplotypes were found, and haplotype 6 (Hap_6, 77%) of pvmsa180 was detected in isolates from six countries.
Conclusions: A novel P. vivax surface protein, PvMSA180, was characterized in this study. Most of P. vivax-infected patients had specific antibodies against particular antigenic domains, indicating that this protein is immunogenic in naturally exposed populations. Genetic analysis of worldwide isolates showed that pvmsa180 is less polymorphic than other well-known candidates and that some haplotypes are common to several countries. However, additional studies with a larger sample size are necessary to evaluate the antibody responses in geographically separated populations, and to identify the function of PvMSA180 during parasite invasion.
Keywords: Haplotype; Humoral immune response; MSA180; Merozoite surface protein; Plasmodium vivax.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of a novel merozoite surface protein of Plasmodium vivax, Pv41.Acta Trop. 2013 Jun;126(3):222-8. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23499861
-
Immunological characterization of Plasmodium vivax Pv32, a novel predicted GPI-anchored merozoite surface protein.Malar J. 2018 Jul 27;17(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2401-7. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 30053874 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of Pv50, a novel Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Apr 18;12(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3434-7. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30999945 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally acquired humoral and cellular immune responses to Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 8 in patients with P. vivax infection.Malar J. 2017 May 22;16(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12936-017-1837-5. Malar J. 2017. PMID: 28532483 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of the Plasmodium vivax thrombospondin-related apical merozoite protein.Malar J. 2010 Oct 13;9:283. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-283. Malar J. 2010. PMID: 20942952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PfMSA180 is a novel Plasmodium falciparum vaccine antigen that interacts with human erythrocyte integrin associated protein (CD47).Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 11;9(1):5923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42366-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30976034 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Malaria: Non-Laverania Plasmodium Biology and Invasion Mechanisms.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 13;10(7):889. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070889. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of merozoite-specific thrombospondin-related anonymous protein (MTRAP) in Plasmodium vivax and P. knowlesi parasites.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Feb 23;14:1354880. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1354880. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38465236 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species reactivity of antibodies against Plasmodium vivax blood-stage antigens to Plasmodium knowlesi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Jun 19;14(6):e0008323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008323. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32559186 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species analysis of apical asparagine-rich protein of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 10;8(1):5781. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23728-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29636493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. World malaria report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

