APOBEC3B cytidine deaminase targets the non-transcribed strand of tRNA genes in yeast
- PMID: 28351647
- PMCID: PMC5450012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.03.003
APOBEC3B cytidine deaminase targets the non-transcribed strand of tRNA genes in yeast
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "APOBEC3B cytidine deaminase targets the non-transcribed strand of tRNA genes in yeast" [DNA Repair 53 (2017) 4-14].DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Aug;80:94-95. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 Jun 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31182349 No abstract available.
Abstract
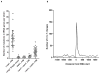
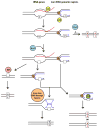
Variations in mutation rates across the genome have been demonstrated both in model organisms and in cancers. This phenomenon is largely driven by the damage specificity of diverse mutagens and the differences in DNA repair efficiency in given genomic contexts. Here, we demonstrate that the single-strand DNA-specific cytidine deaminase APOBEC3B (A3B) damages tRNA genes at a 1000-fold higher efficiency than other non-tRNA genomic regions in budding yeast. We found that A3B-induced lesions in tRNA genes were predominantly located on the non-transcribed strand, while no transcriptional strand bias was observed in protein coding genes. Furthermore, tRNA gene mutations were exacerbated in cells where RNaseH expression was completely abolished (Δrnh1Δrnh35). These data suggest a transcription-dependent mechanism for A3B-induced tRNA gene hypermutation. Interestingly, in strains proficient in DNA repair, only 1% of the abasic sites formed upon excision of A3B-deaminated cytosines were not repaired leading to mutations in tRNA genes, while 18% of these lesions failed to be repaired in the remainder of the genome. A3B-induced mutagenesis in tRNA genes was found to be efficiently suppressed by the redundant activities of both base excision repair (BER) and the error-free DNA damage bypass pathway. On the other hand, deficiencies in BER did not have a profound effect on A3B-induced mutations in CAN1, the reporter for protein coding genes. We hypothesize that differences in the mechanisms underlying ssDNA formation at tRNA genes and other genomic loci are the key determinants of the choice of the repair pathways and consequently the efficiency of DNA damage repair in these regions. Overall, our results indicate that tRNA genes are highly susceptible to ssDNA-specific DNA damaging agents. However, increased DNA repair efficacy in tRNA genes can prevent their hypermutation and maintain both genome and proteome homeostasis.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

