Bats pre-adapt sensory acquisition according to target distance prior to takeoff even in the presence of closer background objects
- PMID: 28352130
- PMCID: PMC5428694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00543-8
Bats pre-adapt sensory acquisition according to target distance prior to takeoff even in the presence of closer background objects
Abstract
Animals execute sensorimotor sequences to optimize performance of complex actions series. However, the sensory aspects of these sequences and their dynamic control are often poorly understood. We trained bats to fly to targets at different distances, and analysed their sensory behavior before and during flight to test whether they assess target distance before flight and how they adapt sensory acquisition in different situations. We demonstrate that bats' sensory acquisition during approach-flight is more flexible than previously described. We identified acoustic parameters that illustrate that bats assess target distance before takeoff. We show that bats adapt their echolocation approach-sequences to target distance - ignoring closer background objects. At shorter distances, bats initiated their echolocation approach-sequence with distance-appropriate parameters, thus entering the approach sensory sequence "in step". Our results suggest that in order to perform fine flight-manoeuvres, bats must maintain their sensorimotor plan in phase. To do this, they adapt acquisition according to target distance before initiating a complex sensory sequence based on a sensorimotor feedback-loop, even in complex acoustic environments, which impose other sensory reactions and restrictions. Though studying this in non-echolocating animals may prove difficult, such mechanisms are probably widely used in nature whenever complex series of sensorimotor actions are required.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
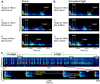
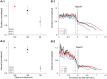
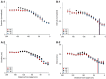
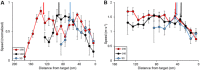
References
-
- Kalko EV, Schnitzler HU. Plasticity in echolocation signals of European pipistrelle bats in search flight: implications for habitat use and prey detection. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1993;33:415–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00170257. - DOI
-
- Obrist MK. Flexible bat echolocation: the influence of individual, habitat and conspecifics on sonar signal design. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1995;36:207–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00177798. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

