Sonidegib: mechanism of action, pharmacology, and clinical utility for advanced basal cell carcinomas
- PMID: 28352196
- PMCID: PMC5360396
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S130910
Sonidegib: mechanism of action, pharmacology, and clinical utility for advanced basal cell carcinomas
Abstract
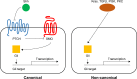
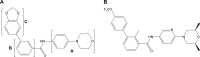
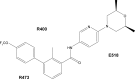
The Hedgehog (Hh) pathway is critical for cell differentiation, tissue polarity, and stem cell maintenance during embryonic development, but is silent in adult tissues under normal conditions. However, aberrant Hh signaling activation has been implicated in the development and promotion of certain types of cancer, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC), medulloblastoma, and gastrointestinal cancers. In 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved sonidegib, a smoothened (SMO) antagonist, for treatment of advanced BCC (aBCC) after a successful Phase II clinical trial. Sonidegib, also named Odomzo, is the second Hh signaling inhibitor approved by the FDA to treat BCCs following approval of the first SMO antagonist vismodegib in 2012. What are the major features of sonidegib (mechanism of action; metabolic profiles, clinical efficacy, safety, and tolerability profiles)? Will the sonidegib experience help other clinical trials using Hh signaling inhibitors in the future? In this review, we will summarize current understanding of BCCs and Hh signaling. We will focus on sonidegib and its use in the clinic, and we will discuss ways to improve its clinical application in cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: Hedgehog; basal cell carcinoma; cancer; inhibitor; smoothened; sonidegib.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in drosophila. Nature. 1980;287(5785):795–801. - PubMed
-
- Krauss S, Concordet JP, Ingham PW. A functionally conserved homolog of the drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell. 1993;75(7):1431–1444. - PubMed
-
- Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, et al. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993;75(7):1417–1430. - PubMed
-
- Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993;75(7):1401–1416. - PubMed
-
- Chang DT, Lopez A, von Kessler DP, et al. Products, genetic linkage and limb patterning activity of a murine hedgehog gene. Development. 1994;120(11):3339–3353. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

