Color duplex ultrasonography findings of temporal arteries in a case of giant cell arteritis: role in diagnosis and follow-up
- PMID: 28352206
- PMCID: PMC5359129
- DOI: 10.2147/OARRR.S110585
Color duplex ultrasonography findings of temporal arteries in a case of giant cell arteritis: role in diagnosis and follow-up
Abstract
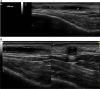
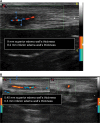
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that affects medium- and large-sized arteries. The diagnostic gold standard is the temporal artery biopsy, but it has limited sensitivity and some difficulties in reproducibility. Color duplex ultrasonography is a noninvasive, reproducible, and inexpensive method for diagnosis of temporal arteries involvement (temporal arteritis [TA]) in GCA with high sensitivity and specificity. We present the ultrasound findings at baseline and during follow-up in a case of TA in a patient with GCA.
Keywords: GCA; color duplex ultrasonography; halo sign; temporal arteries; temporal arteritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Limited value of temporal artery ultrasonography examinations for diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: analysis of 77 subjects.J Rheumatol. 2010 Nov;37(11):2326-30. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.100353. Epub 2010 Sep 1. J Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20810501
-
Colour-duplex ultrasonography of the temporal and ophthalmic arteries in the diagnosis and follow-up of giant cell arteritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009 Jan-Feb;27(1 Suppl 52):S77-82. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19646351
-
Colour duplex sonography of temporal arteries before decision for biopsy: a prospective study in 55 patients with suspected giant cell arteritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(4):R116. doi: 10.1186/ar2003. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16859533 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical duplex ultrasound for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis with vertebral artery involvement.J Neuroimaging. 2021 Jul;31(4):656-664. doi: 10.1111/jon.12857. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Neuroimaging. 2021. PMID: 33817861 Review.
-
Accuracy of Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Adv Rheumatol. 2023 Feb 8;63(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s42358-023-00286-3. Adv Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36755336
Cited by
-
Blood Biomarkers for Monitoring and Prognosis of Large Vessel Vasculitides.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021 Feb 10;23(3):17. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-00980-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33569633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound versus temporal artery biopsy in patients with Giant cell arteritis: a prospective cohort study.BMC Med Imaging. 2019 Jun 6;19(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12880-019-0344-2. BMC Med Imaging. 2019. Retraction in: BMC Med Imaging. 2020 May 21;20(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12880-020-00454-7. PMID: 31170909 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Hunder GG. The early history of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. First descriptions to 1970. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81(8):1071–1083. - PubMed
-
- Hellmann DB. Giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. In: Imboden JB, Hellmann DB, Stone JH, editors. Current Rheumatology Diagnosis and Treatment. New York, NY: Mc Graw Hill; 2004. pp. 235–241.
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymalgia rheumatica. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(6):505–515. - PubMed
-
- Hall JK, Volpe NJ, Galetta SL, Liu GT, Syed NA, Balcer LJ. The role of unilateral temporal artery biopsy. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(3):543–548. discussion 548. - PubMed
-
- Ball EL, Walsh SR, Tang TY, Gohil R, Clarke JM. Role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of temporal arteritis. Br J Surg. 2010;97(12):1765–1771. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

