Effects of Traumatic Stress Induced in the Juvenile Period on the Expression of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Type A Subunits in Adult Rat Brain
- PMID: 28352479
- PMCID: PMC5352903
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5715816
Effects of Traumatic Stress Induced in the Juvenile Period on the Expression of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Type A Subunits in Adult Rat Brain
Abstract
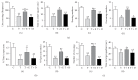
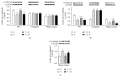
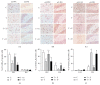
Studies have found that early traumatic experience significantly increases the risk of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) deficits were proposed to be implicated in development of PTSD, but the alterations of GABA receptor A (GABAAR) subunits induced by early traumatic stress have not been fully elucidated. Furthermore, previous studies suggested that exercise could be more effective than medications in reducing severity of anxiety and depression but the mechanism is unclear. This study used inescapable foot-shock to induce PTSD in juvenile rats and examined their emotional changes using open-field test and elevated plus maze, memory changes using Morris water maze, and the expression of GABAAR subunits (γ2, α2, and α5) in subregions of the brain in the adulthood using western blotting and immunohistochemistry. We aimed to observe the role of GABAAR subunits changes induced by juvenile trauma in the pathogenesis of subsequent PTSD in adulthood. In addition, we investigated the protective effects of exercise for 6 weeks and benzodiazepine (clonazepam) for 2 weeks. This study found that juvenile traumatic stress induced chronic anxiety and spatial memory loss and reduced expression of GABAAR subunits in the adult rat brains. Furthermore, exercise led to significant improvement as compared to short-term BZ treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Anda R. F., Felitti V. J., Bremner J. D., et al. The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood: a convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 2006;256(3):174–186. doi: 10.1007/s00406-005-0624-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lydiard R. B. The role of GABA in anxiety disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2003;64(supplement 3):21–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

