Safety of a Rapidly Dissolving Buprenorphine/Naloxone Sublingual Tablet (BNX-RDT) for Treatment of Opioid Dependence: A Multicenter, Open-label Extension Study
- PMID: 28353467
- PMCID: PMC5457835
- DOI: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000301
Safety of a Rapidly Dissolving Buprenorphine/Naloxone Sublingual Tablet (BNX-RDT) for Treatment of Opioid Dependence: A Multicenter, Open-label Extension Study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the safety of rapidly dissolving buprenorphine/naloxone sublingual tablets (BNX-RDT) in opioid-dependent patients.
Methods: This open-label, 24-week extension study enrolled patients who completed primary trials of BNX-RDT. Daily tablet doses ranged from 5.7 to 17.1 mg. The primary endpoint was safety; secondary assessments included opioid cravings, addiction severity, health-related quality of life (QOL), and workplace productivity at screening (final day of the primary trials) through study end, with changes measured from baseline of the primary trials.
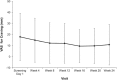
Results: In all, 665 patients received treatment; 292 (43.9%) completed the study. A total of 258 patients (38.8%) reported 557 treatment-emergent adverse events, most commonly headache (3.2%) and constipation (3.0%). Craving scores showed continued improvement on 100-mm visual analog scale (mean change from primary trial baseline, -52.8 at screening; mean change from extension trial baseline, -60.5 at week 24). Reductions in addiction severity from baseline of both the primary and extension trial were maintained through week 24 on multiple assessments, as were improvements in QOL on Short Form 36. Employment increased by 15% and mean (SD) hours worked per week increased by 4.6 (20.1) from baseline to study end. Mean (SD) scores for impact of opioid dependence on work productivity improved from 4.7 (3.0) at baseline to 0.9 (1.8) at study end (11-point scale).
Conclusions: Extended treatment with BNX-RDT demonstrated a safety profile similar to other BNX formulations, reduced opioid cravings, and improved both QOL and work productivity. Continued treatment may enable patients to advance in recovery and return to normal functioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Kent Hoffman, DO, has received speaker's honoraria from Alkermes, Orexo, Bio Delivery Sciences Inc., and Iroko; has received clinical research grants (primary investigator) from Orexo, Bio Delivery Sciences Inc., Reckitt Benckiser, Alkermes, and Braeburn; and has been a remunerated advisor/consultant for Orexo, Bio Delivery Sciences Inc., and Braeburn. Marvin L. Peyton, MD, has received clinical research grants from Alkermes, Allergan, Appian International Research, AssureRxHealth, Astra Zeneca, Braeburn, Cephalon, Daiichi Sankyo, Elan, Euthymics Bioscience, Forest Research Institute, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Lundbeck, MedImmune, Novartis, Orexo, Otsuka, Palatin Technologies, Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, Roche, Sepacor, Shire, Sunovion, Takeda, and TauRx Therapeutics, and has received honoraria from Orexo. Michael Sumner, MB, BS, MRCP (UK) is an employee of Orexo US, Inc., Morristown, NJ.
Figures

References
-
- Apelt SM, Scherbaum N, Golz J, et al. Safety, effectiveness and tolerance of buprenorphine-naloxone in the treatment of opioid dependence: results from a nationwide non-interventional study in routine care. Pharmacopsychiatry 2013; 46:94–107. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum HG, White AG, Schiller M, et al. Societal costs of prescription opioid abuse, dependence, and misuse in the United States. Pain Med 2011; 12:657–667. - PubMed
-
- Cacciola JS, Alterman AI, McLellan AT, et al. Initial evidence for the reliability and validity of a “Lite” version of the Addiction Severity Index. Drug Alcohol Depend 2007; 87:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Feelemyer JP, Des Jarlais DC, Arasteh K, et al. Changes in quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) and addiction severity index (ASI) among participants in opioid substitution treatment (OST) in low and middle income countries: an international systematic review. Drug Alcohol Depend 2014; 134:251–258. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fischer A, Johansson K, Gruden S. Zubsolv®: a novel sublingual tablet with improved bioavailability of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid dependence [poster]. Presented at: Annual Conference of the Association for Medical Education and Research in Substance Abuse; November 6-7, 2014; San Francisco, CA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

