Effects of Simulated Hearing Loss on Bilingual Children's Consonant Recognition in Noise
- PMID: 28353522
- PMCID: PMC5570634
- DOI: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000428
Effects of Simulated Hearing Loss on Bilingual Children's Consonant Recognition in Noise
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the possible impact of simulated hearing loss on speech perception in Spanish-English bilingual children. To avoid confound between individual differences in hearing-loss configuration and linguistic experience, threshold-elevating noise simulating a mild-to-moderate sloping hearing loss was used with normal-hearing listeners. The hypotheses were that: (1) bilingual children can perform similarly to English-speaking monolingual peers in quiet; (2) for both bilingual and monolingual children, noise and simulated hearing loss would have detrimental impacts consistent with their acoustic characteristics (i.e., consonants with high-frequency cues remain highly intelligible in speech-shaped noise, but suffer from simulated hearing loss more than other consonants); (3) differences in phonology and acquisition order between Spanish and English would have additional negative influence on bilingual children's recognition of some English consonants.
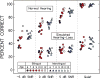
Design: Listeners were 11 English-dominant, Spanish-English bilingual children (6 to 12 years old) and 12 English-speaking, monolingual age peers. All had normal hearing and age-appropriate nonverbal intelligence and expressive English vocabulary. Listeners performed a listen-and-repeat speech perception task. Targets were 13 American English consonants embedded in vowel-consonant-vowel (VCV) syllables. VCVs were presented in quiet and in speech-shaped noise at signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of -5, 0, 5 dB (normal-hearing condition). For the simulated hearing-loss condition, threshold-elevating noise modeling a mild-to-moderate sloping sensorineural hearing loss profile was added to the normal-hearing stimuli for 0, 5 dB SNR, and quiet. Responses were scored for consonant correct. Individual listeners' performance was summarized for average across 13 consonants (overall) and for individual consonants.
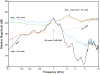
Results: Groups were compared for the effects of background noise and simulated hearing loss. As predicted, group performed similarly in quiet. The simulated hearing loss had a considerable detrimental impact on both groups, even in the absence of speech-shaped noise. Contrary to our prediction, no group difference was observed at any SNR in either condition. However, although nonsignificant, the greater within-group variance for the bilingual children in the normal-hearing condition indicated a wider "normal" range than for the monolingual children. Interestingly, although it did not contribute to the group difference, bilingual children's overall consonant recognition in both conditions improved with age, whereas such a developmental trend for monolingual children was observed only in the simulated hearing-loss condition, suggesting possible effects of experience. As for the recognition of individual consonants, the influence of background noise or simulated hearing loss was similar between groups and was consistent with the prediction based on their acoustic characteristics.
Conclusions: The results demonstrated that school-age, English-dominant, Spanish-English bilingual children can recognize English consonants in a background of speech-shaped noise with similar average accuracy as English-speaking monolingual age peers. The general impact of simulated hearing loss was also similar between bilingual and monolingual children. Thus, our hypothesis that bilingual children's English consonant recognition would suffer from background noise or simulated hearing loss more than the monolingual peers was rejected. However, the present results raise several issues that warrant further investigation, including the possible difference in the "normal" range for bilingual and monolingual children, influence of experience, impact of actual hearing loss on bilingual children, and stimulus quality.
Figures


References
-
- American National Standards Institute [ANSI] Methods for Calculation of the Speech Intelligibility Index. New York, NY: Author; 1997. ANSI/ASA S3.5-1997.
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association [ASHA] ASHA summary membership and affiliation counts, year-end 2015. 2016a Retrieved on July 8 2016 from: www.asha.org/uploadedFiles/2015-Member-Counts.pdf.
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association [ASHA] Demographic profile of ASHA members providing bilingual services. 2016b Retrieved on July 6 2016 from: www.asha.org/uploadedFiles/Demographic-Profile-Bilingual-Spanish-Service....
-
- Boothroyd A. Computer-Assisted Speech Perception Assessment (CASPA) 5.0. Software; San Diego, CA: 2008.
-
- Brown L, Sherbenou RJ, Johnsen SK. Test of Nonverbal Intelligence (4th ed) [TONI-4] Austin, TX: Pro-Ed; 2010.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

