Vitamin D Insufficiency Exacerbates Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration and Decreases AMPK/SIRT1 Activity in Obese Rats
- PMID: 28353634
- PMCID: PMC5409677
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9040338
Vitamin D Insufficiency Exacerbates Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration and Decreases AMPK/SIRT1 Activity in Obese Rats
Abstract
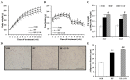
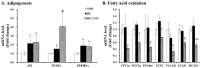
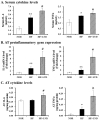
Obesity is recognized as a state of chronic low-grade systemic inflammation due to adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and production of proinflammatory adipokines. Decreased vitamin D status is associated with obesity. The specific aim of the present study is to investigate the effects of vitamin D on obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomized and fed a normal diet (NOR, 1000 IU vitamin D/kg diet), a 45% high-fat diet (HF, 1000 IU vitamin D/kg diet), or a 45% high-fat diet containing 25 IU vitamin D/kg diet (HF+LVD) for 12 weeks. The vitamin D-insufficient diet (HF+LVD) led to vitamin D inadequacy as determined by serum 25(OH)D level, 68.56 ± 7.97 nmol/L. The HF+LVD group exacerbated HF-increased adipocyte size, adipogenic gene expression of PPARγ, adipose tissue macrophage recruitment, and proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and TNFα levels in epididymal white adipose tissue. In addition, vitamin D insufficiency significantly decreased mRNA levels of β-oxidation-related genes such as CPT1α, PGC1α, PPARα, VLCAD, LCAD, MCAD, and UCP1. Moreover, significant decrements of SIRT1 and AMPK activity were noted in obese rats fed with a vitamin D-insufficient diet. The observed deleterious effects of vitamin D insufficiency on adipose tissue expansion, immune cell infiltration and inflammatory status suggest vitamin D plays a beneficial role in adipocyte metabolic metabolism and obesity progression. SIRT1 and AMPK activity may play a role in the mechanism of vitamin D action.
Keywords: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK); adipose tissue macrophage infiltration; obesity; sirtulin 1 (SIRT1); vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

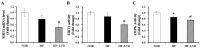
References
-
- Xu H., Barnes G.T., Yang Q., Tan G., Yang D., Chou C.J., Sole J., Nichols A., Ross J.S., Tartaglia L.A., et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003;112:1821–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI200319451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

