Effects of different lower-limb sensory stimulation strategies on postural regulation-A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28355265
- PMCID: PMC5371369
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174522
Effects of different lower-limb sensory stimulation strategies on postural regulation-A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Systematic reviews of balance control have tended to only focus on the effects of single lower-limb stimulation strategies, and a current limitation is the lack of comparison between different relevant stimulation strategies. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to examine evidence of effects of different lower-limb sensory stimulation strategies on postural regulation and stability. Moderate- to high- pooled effect sizes (Unbiased (Hedges' g) standardized mean differences (SMD) = 0.31-0.66) were observed with the addition of noise in a Stochastic Resonance Stimulation Strategy (SRSS), in three populations (i.e., healthy young adults, older adults, and individuals with lower-limb injuries), and under different task constraints (i.e., unipedal, bipedal, and eyes open). A Textured Material Stimulation Strategy (TMSS) enhanced postural control in the most challenging condition-eyes-closed on a stable surface (SMD = 0.61), and in older adults (SMD = 0.30). The Wearable Garments Stimulation Strategy (WGSS) showed no or adverse effects (SMD = -0.68-0.05) under all task constraints and in all populations, except in individuals with lower-limb injuries (SMD = 0.20). Results of our systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that future research could consider combining two or more stimulation strategies in intervention treatments for postural regulation and balance problems, depending on individual needs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
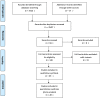




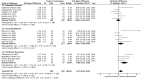




References
-
- Corbin DM, Hart JM, McKeon PO, Palmieri-Smith R, Ingersoll CD, Hertel J. The effect of textured insoles on postural control in double and single limb stance. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. 2007;16(4):363–72. - PubMed
-
- Menant JC, Steele JR, Menz HB, Munro BJ, Lord SR. Optimizing footwear for older people at risk of falls. Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development. 2008;45(8):1167–82. - PubMed
-
- Hijmans JM, Geertzen JHB, Dijkstra PU, Postema K. A systematic review of the effects of shoes and other ankle or foot appliances on balance in older people and people with peripheral nervous system disorders. Gait & Posture. 2007;25(2):316–23. - PubMed
-
- Hlavackova P, Vuillerme N. Do somatosensory conditions from the foot and ankle affect postural responses to plantar-flexor muscles fatigue during bipedal quiet stance? Gait & Posture. 2012;36(1):16–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

