Mining expression and prognosis of topoisomerase isoforms in non-small-cell lung cancer by using Oncomine and Kaplan-Meier plotter
- PMID: 28355294
- PMCID: PMC5371362
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174515
Mining expression and prognosis of topoisomerase isoforms in non-small-cell lung cancer by using Oncomine and Kaplan-Meier plotter
Abstract
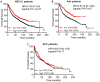
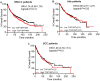
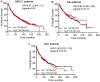
DNA topoisomerases are essential to modulate DNA topology during various cellular genetic processes. The expression and distinct prognostic value of topoisomerase isoforms in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is not well established. In the current study, we have examined the mRNA expression of topoisomerase isoforms by using Oncomine analysis and investigated their prognostic value via the Kaplan-Meier plotter database in NSCLC patients. Our analysis indicated that the expression level of topoisomerases in lung cancer was higher compared with normal tissues. Especially, high expression of two topoisomerase isoforms, TOP2A and TOP3A, was found to be correlated to worse overall survival (OS) in all NSCLC and lung adenocarcinoma (Ade) patients, but not in lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) patients. In a contrast, high expression of isoforms TOP1 and TOP2B indicated better OS in all NSCLC and Ade, but not in SCC patients. Meanwhile, high expression of TOP1MT and TOP3B was not correlated with OS in NSCLC patients. Furthermore, we also demonstrated a relationship between topoisomerase isoforms and the clinicopathological features for the NSCLC patients, such as grades, clinical stages, lymph node status, smoking status, gender, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. These results support that TOP2A and TOP3A are associated with worse prognosis in NSCLC patients. In addition, our study also shows that TOP1 and TOP2B contribute to favorable prognosis in NSCLC patients. The exact prognostic significance of TOP1MT and TOP3B need to be further elucidated. Comprehensive evaluation of expression and prognosis of topoisomerase isoforms will be a benefit for the better understanding of heterogeneity and complexity in the molecular biology of NSCLC, paving a way for more accurate prediction of prognosis and discovery of potential drug targets for NSCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

