Genome-wide association analysis identifies resistance loci for bacterial blight in a diverse collection of indica rice germplasm
- PMID: 28355306
- PMCID: PMC5371361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174598
Genome-wide association analysis identifies resistance loci for bacterial blight in a diverse collection of indica rice germplasm
Abstract
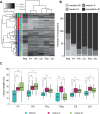
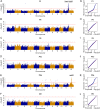
Bacterial blight, which is caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), is one of the most devastating rice diseases worldwide. The development and use of disease-resistant cultivars have been the most effective strategy to control bacterial blight. Identifying the genes mediating bacterial blight resistance is a prerequisite for breeding cultivars with broad-spectrum and durable resistance. We herein describe a genome-wide association study involving 172 diverse Oryza sativa ssp. indica accessions to identify loci influencing the resistance to representative strains of six Xoo races. Twelve resistance loci containing 121 significantly associated signals were identified using 317,894 single nucleotide polymorphisms, which explained 13.3-59.9% of the variability in lesion length caused by Xoo races P1, P6, and P9a. Two hotspot regions (L11 and L12) were located within or nearby two cloned R genes (xa25 and Xa26) and one fine-mapped R gene (Xa4). Our results confirmed the relatively high resolution of genome-wide association studies. Moreover, we detected novel significant associations on chromosomes 2, 3, and 6-10. Haplotype analyses of xa25, the Xa26 paralog (MRKc; LOC_Os11g47290), and a Xa4 candidate gene (LOC_11g46870) revealed differences in bacterial blight resistance among indica subgroups. These differences were responsible for the observed variations in lesion lengths resulting from infections by Xoo races P1 and P9a. Our findings may be relevant for future studies involving bacterial blight resistance gene cloning, and provide insights into the genetic basis for bacterial blight resistance in indica rice, which may be useful for knowledge-based crop improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Zhang Q. Genetic evaluation and utilization of resistance to rice bacterial blight in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 1991;24(2):26–36.
-
- Khush GS, Mackill DJ, Sidhu GS. Breeding rice for resistance to bacterial blight In: Banta SJ, editor. Bacterial Blight of Rice. Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute; 1989. p. 207–17.
-
- Ogawa T. Methods and strategy for monitoring race distribution and identification of resistance genes to bacterial leaf blight (Xanthomonas campetris pv. oryzae) in rice. JARQ-Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly. 1993;27:71–80.
-
- Mew TW. Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 1987;25:359–82.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

