Therapy of tacrolimus combined with corticosteroids in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 28355356
- PMCID: PMC5423753
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20175976
Therapy of tacrolimus combined with corticosteroids in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
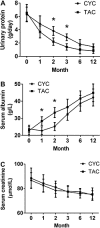
We evaluated the efficacy and safety of tacrolimus (TAC) combined with corticosteroids in treating patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). One hundred seventy-seven biopsy-proven IMN patients were recruited in this retrospective clinical study. Sixty patients received TAC (target blood concentration of 4-8 ng/mL) and 117 patients received daily cyclophosphamide (CYC, 100 mg) combined with prednisone. Remission rates at the end of the first, second and third month in the TAC group were significantly higher than that in the CYC group (1st: 35.0 vs 19.7%, P<0.05; 2nd: 56.7 vs 38.5%, P<0.05; 3rd: 76.7 vs 59.0%, P<0.05). In the first 3 months, daily urinary protein and serum albumin in the TAC group obtained a better improvement than that in the CYC group (P<0.05). At the end of the sixth and the twelfth month, the remission rates, daily urinary protein and serum albumin were all comparable between the two groups (P>0.05). No significant difference of relapse rate between the groups was found (16.3 vs 12.0%, P>0.05). Patients were more likely to develop glucose intolerance in the TAC group. The TAC regimen obtained more benefits in treating IMN patients, especially in the first 3 months, than the CYC regimen.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical