Opposing Intermolecular Tuning of Ca2+ Affinity for Calmodulin by Neurogranin and CaMKII Peptides
- PMID: 28355539
- PMCID: PMC5374985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.01.020
Opposing Intermolecular Tuning of Ca2+ Affinity for Calmodulin by Neurogranin and CaMKII Peptides
Abstract
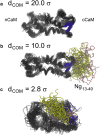
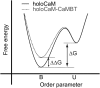
We investigated the impact of bound calmodulin (CaM)-target compound structure on the affinity of calcium (Ca2+) by integrating coarse-grained models and all-atomistic simulations with nonequilibrium physics. We focused on binding between CaM and two specific targets, Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and neurogranin (Ng), as they both regulate CaM-dependent Ca2+ signaling pathways in neurons. It was shown experimentally that Ca2+/CaM (holoCaM) binds to the CaMKII peptide with overwhelmingly higher affinity than Ca2+-free CaM (apoCaM); the binding of CaMKII peptide to CaM in return increases the Ca2+ affinity for CaM. However, this reciprocal relation was not observed in the Ng peptide (Ng13-49), which binds to apoCaM or holoCaM with binding affinities of the same order of magnitude. Unlike the holoCaM-CaMKII peptide, whose structure can be determined by crystallography, the structural description of the apoCaM-Ng13-49 is unknown due to low binding affinity, therefore we computationally generated an ensemble of apoCaM-Ng13-49 structures by matching the changes in the chemical shifts of CaM upon Ng13-49 binding from nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Next, we computed the changes in Ca2+ affinity for CaM with and without binding targets in atomistic models using Jarzynski's equality. We discovered the molecular underpinnings of lowered affinity of Ca2+ for CaM in the presence of Ng13-49 by showing that the N-terminal acidic region of Ng peptide pries open the β-sheet structure between the Ca2+ binding loops particularly at C-domain of CaM, enabling Ca2+ release. In contrast, CaMKII peptide increases Ca2+ affinity for the C-domain of CaM by stabilizing the two Ca2+ binding loops. We speculate that the distinctive structural difference in the bound complexes of apoCaM-Ng13-49 and holoCaM-CaMKII delineates the importance of CaM's progressive mechanism of target binding on its Ca2+ binding affinities.
Copyright © 2017 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 23;19(9):2495. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092495. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30142967 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of calmodulin mutants with up to 900-fold increase in binding specificity.J Mol Biol. 2009 Feb 6;385(5):1470-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.053. Epub 2008 Sep 27. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18845160
-
Site-specific modification of calmodulin Ca²(+) affinity tunes the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor activation profile.Biochem J. 2010 Nov 15;432(1):89-99. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100505. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20815817
-
Neuronal CA2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of structure and autoregulation in cellular function.Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:473-510. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135410. Epub 2001 Nov 9. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12045104 Review.
-
Calmodulin-Binding Proteins in Muscle: A Minireview on Nuclear Receptor Interacting Protein, Neurogranin, and Growth-Associated Protein 43.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3):1016. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031016. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32033037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A mutually induced conformational fit underlies Ca2+-directed interactions between calmodulin and the proximal C terminus of KCNQ4 K+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 12;294(15):6094-6112. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006857. Epub 2019 Feb 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30808708 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the atomic charge of calcium ion requires the information of its coordination geometry in an EF-hand motif.J Chem Phys. 2021 Mar 28;154(12):124104. doi: 10.1063/5.0037517. J Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 33810667 Free PMC article.
-
A Mitochondrial Localized Chaperone Regulator OsBAG6 Functions in Saline-Alkaline Stress Tolerance in Rice.Rice (N Y). 2024 Jan 22;17(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12284-024-00686-z. Rice (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38252225 Free PMC article.
-
Metal cofactor modulated folding and target recognition of HIV-1 NCp7.PLoS One. 2018 May 1;13(5):e0196662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196662. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29715277 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium mediated static and dynamic allostery in S100A12: Implications for target recognition by S100 proteins.Protein Sci. 2024 Apr;33(4):e4955. doi: 10.1002/pro.4955. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38501487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gifford J.L., Walsh M.P., Vogel H.J. Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem. J. 2007;405:199–221. - PubMed
-
- Yamniuk A.P., Vogel H.J. Calmodulin’s flexibility allows for promiscuity in its interactions with target proteins and peptides. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004;27:33–57. - PubMed
-
- Xia Z., Storm D.R. The role of calmodulin as a signal integrator for synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;6:267–276. - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II--discovery, progress in a quarter of a century, and perspective: implication for learning and memory. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005;28:1342–1354. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

