SMARCAD1 Contributes to the Regulation of Naive Pluripotency by Interacting with Histone Citrullination
- PMID: 28355564
- PMCID: PMC5466819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.070
SMARCAD1 Contributes to the Regulation of Naive Pluripotency by Interacting with Histone Citrullination
Abstract
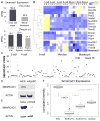
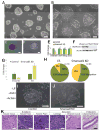
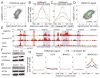
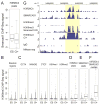
Histone citrullination regulates diverse cellular processes. Here, we report that SMARCAD1 preferentially associates with H3 arginine 26 citrullination (H3R26Cit) peptides present on arrays composed of 384 histone peptides harboring distinct post-transcriptional modifications. Among ten histone modifications assayed by ChIP-seq, H3R26Cit exhibited the most extensive genomewide co-localization with SMARCAD1 binding. Increased Smarcad1 expression correlated with naive pluripotency in pre-implantation embryos. In the presence of LIF, Smarcad1 knockdown (KD) embryonic stem cells lost naive state phenotypes but remained pluripotent, as suggested by morphology, gene expression, histone modifications, alkaline phosphatase activity, energy metabolism, embryoid bodies, teratoma, and chimeras. The majority of H3R26Cit ChIP-seq peaks occupied by SMARCAD1 were associated with increased levels of H3K9me3 in Smarcad1 KD cells. Inhibition of H3Cit induced H3K9me3 at the overlapping regions of H3R26Cit peaks and SMARCAD1 peaks. These data suggest a model in which SMARCAD1 regulates naive pluripotency by interacting with H3R26Cit and suppressing heterochromatin formation.
Keywords: ChIP-seq; SMARCAD1; citrullination; histone modification; naive state; pluripotency; protein array; stem cells.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- ACTIVEMOTIF. MODified(TM) Histone peptide Array Manual. 2014 Available: http://www.activemotif.com/documents/1691.pdf.
-
- ADRA CN, DONATO JL, BADOVINAC R, SYED F, KHERAJ R, CAI H, MORAN C, KOLKER MT, TURNER H, WEREMOWICZ S, SHIRAKAWA T, MORTON CC, SCHNIPPER LE, DREWS R. SMARCAD1, a novel human helicase family-defining member associated with genetic instability: cloning, expression, and mapping to 4q22-q23, a band rich in breakpoints and deletion mutants involved in several human diseases. Genomics. 2000;69:162–73. - PubMed
-
- BRONS IG, SMITHERS LE, TROTTER MW, RUGG-GUNN P, SUN B, CHUVA DE SOUSA LOPES SM, HOWLETT SK, CLARKSON A, AHRLUND-RICHTER L, PEDERSEN RA, VALLIER L. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448:191–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

