Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Hypothalamic Cell Diversity
- PMID: 28355573
- PMCID: PMC5782816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.004
Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Hypothalamic Cell Diversity
Abstract
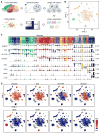
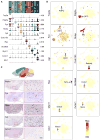
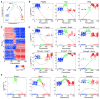
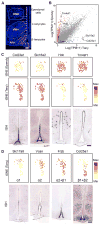
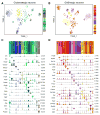
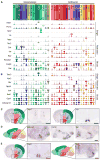
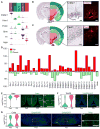
The hypothalamus is one of the most complex brain structures involved in homeostatic regulation. Defining cell composition and identifying cell-type-specific transcriptional features of the hypothalamus is essential for understanding its functions and related disorders. Here, we report single-cell RNA sequencing results of adult mouse hypothalamus, which defines 11 non-neuronal and 34 neuronal cell clusters with distinct transcriptional signatures. Analyses of cell-type-specific transcriptomes reveal gene expression dynamics underlying oligodendrocyte differentiation and tanycyte subtypes. Additionally, data analysis provides a comprehensive view of neuropeptide expression across hypothalamic neuronal subtypes and uncover Crabp1+ and Pax6+ neuronal populations in specific hypothalamic sub-regions. Furthermore, we found food deprivation exhibited differential transcriptional effects among the different neuronal subtypes, suggesting functional specification of various neuronal subtypes. Thus, the work provides a comprehensive transcriptional perspective of adult hypothalamus, which serves as a valuable resource for dissecting cell-type-specific functions of this complex brain region.
Keywords: cell heterogeneity; hypothalamus; neuron diversity; oligodendrocyte; single-cell RNA-seq; tanycyte.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR. Isolation and culture of adult neurons and neurospheres. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:1490–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

