Strengthening health security at the Hajj mass gatherings: characteristics of the infectious diseases surveillance systems operational during the 2015 Hajj
- PMID: 28355612
- PMCID: PMC7107526
- DOI: 10.1093/jtm/taw087
Strengthening health security at the Hajj mass gatherings: characteristics of the infectious diseases surveillance systems operational during the 2015 Hajj
Abstract
Background: Hajj is one of the largest and the most ethnically and culturally diverse mass gatherings worldwide. The use of appropriate surveillance systems ensures timely information management for effective planning and response to infectious diseases threats during the pilgrimage. The literature describes infectious diseases prevention and control strategies for Hajj but with limited information on the operations and characteristics of the existing Hajj infectious diseases surveillance systems.
Method: We reviewed documents, including guidelines and reports from the Saudi Ministry of Health's database, to describe the characteristics of the infectious diseases surveillance systems that were operational during the 2015 Hajj, highlighting best practices and gaps and proposing strategies for strengthening and improvement. Using Pubmed and Embase online search engines and a combination of search terms including, 'mass gatherings' 'Olympics' 'surveillance' 'Hajj' 'health security', we explored the existing literature and highlighted some lessons learnt from other international mass gatherings.
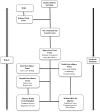
Results: A regular indicator-based infectious disease surveillance system generates routine reports from health facilities within the Kingdom to the regional and central public health directorates all year round. During Hajj, enhanced indicator-based notifiable diseases surveillance systems complement the existing surveillance tool to ensure timely reporting of event information for appropriate action by public health officials.
Conclusion: There is need to integrate the existing Hajj surveillance data management systems and to implement syndromic surveillance as an early warning system for infectious disease control during Hajj. International engagement is important to strengthen Hajj infectious diseases surveillance and to prevent disease transmission and globalization of infectious agents which could undermine global health security.
Keywords: Hajj; infectious diseases; mass gatherings; outbreak; surveillance.
© International Society of Travel Medicine, 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strengthening health security at the Hajj mass gatherings: a Harmonised Hajj Health Information System.J Travel Med. 2018 Jan 1;25(1). doi: 10.1093/jtm/tay070. J Travel Med. 2018. PMID: 30137404 No abstract available.
-
The annual Hajj pilgrimage-minimizing the risk of ill health in pilgrims from Europe and opportunity for driving the best prevention and health promotion guidelines.Int J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun;47:79-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Int J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27343984 Free PMC article.
-
Hajj: infectious disease surveillance and control.Lancet. 2014 Jun 14;383(9934):2073-2082. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60381-0. Epub 2014 May 20. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24857703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of public health security in Saudi Arabia for the 2009 Hajj in response to pandemic influenza A H1N1.Lancet. 2009 Nov 21;374(9703):1786-91. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61927-9. Epub 2009 Nov 14. Lancet. 2009. PMID: 19914707 Review.
-
Vaccinations for Hajj: Enhancing health and global health security.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2025 Jan-Feb;63:102784. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2024.102784. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39579838 Review.
Cited by
-
Digital Response During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Sep 1;22(9):e19338. doi: 10.2196/19338. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32790642 Free PMC article.
-
Health Risk Behaviors and Associated Factors Among Hajj 2024 Pilgrims: A Multinational Cross-Sectional Study.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Jul 2;18:2233-2245. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S521097. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 40621425 Free PMC article.
-
Risk management and infection control preparedness of Saudi healthcare facilities to overcome the COVID-19 pandemic.IJID Reg. 2022 Jun;3:268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 Apr 28. IJID Reg. 2022. PMID: 35720150 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Public Health Digital Surveillance Systems for Infectious Disease Prevention and Control at Mass Gatherings: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 May 19;25:e44649. doi: 10.2196/44649. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37204833 Free PMC article.
-
MERS: What is the current situation in Saudi Arabia?J Travel Med. 2018 Jan 1;25(1):tay065. doi: 10.1093/jtm/tay065. J Travel Med. 2018. PMID: 30107590 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Farid M. The pilgrimage and its implications in a regional malaria eradication programme. WHO/EMRO Inter-Regional Conference on Malaria for the Eastern Mediterranean and European Regions; 1956 Apr World Health Organization report WHO/MAL/168, 1956.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical