Limitations and opportunities of whole blood bilirubin measurements by GEM premier 4000®
- PMID: 28356083
- PMCID: PMC5372304
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-017-0842-8
Limitations and opportunities of whole blood bilirubin measurements by GEM premier 4000®
Abstract
Background: Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia has traditionally been screened by either total serum bilirubin or transcutaneous bilirubin. Whole blood bilirubin (TwB) by the GEM Premier 4000® blood gas analyzer (GEM) is a relatively new technology and it provides fast bilirubin results with a small sample volume and can measure co-oximetry and other analytes. Our clinical study was to evaluate the reliability of TwB measured by the GEM and identify analytical and clinical factors that may contribute to possible bias.
Methods: 440 consecutive healthy newborn samples that had plasma bilirubin ordered for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia screening were included. TwB was first measured using the GEM, after which the remainder of the blood was spun and plasma neonatal bilirubin was measured using the VITROS 5600® (VITROS).
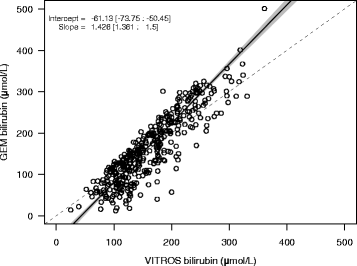
Results: 62 samples (14%) were excluded from analysis due to failure in obtaining GEM results. Passing-Bablok regression suggested that the GEM results were negatively biased at low concentrations of bilirubin and positively biased at higher concentrations relative to the VITROS results (y = 1.43x-61.13). Bland-Altman plots showed an overall negative bias of the GEM bilirubin with a wide range of differences compared to VITROS. Both hemoglobin concentration and hemolysis affected the accuracy of the GEM results. Clinically, male infants had higher mean bilirubin levels, and infants delivered by caesarean section had lower hemoglobin levels. When comparing the number of results below the 40th percentile and above the 95th percentile cut-offs in the Bhutani nomogram which would trigger discharge or treatment, GEM bilirubin exhibited poor sensitivity and poor specificity in contrast to VITROS bilirubin.
Conclusions: An imperfect correlation was observed between whole blood bilirubin measured on the GEM4000® and plasma bilirubin on the VITROS 5600®. The contributors to the observed differences between the two instruments were specimen hemolysis and the accuracy of hemoglobin measurements, the latter of which affects the calculation of plasma-equivalent bilirubin. Additionally, the lack of standardization of total bilirubin calibration particularly in newborn specimens, may also account for some of the disagreement in results.
Keywords: Hyperbilirubinemia; Neonatal; Screening; Whole blood bilirubin.
Figures


References
-
- Raimondi F, Ferrara T, Borrelli AC, Schettino D, Parrella C, Capasso L. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: a critical appraisal of current guidelines and evidence. J Pediatr Neonatal individualized Med. 2012;1(1):25–32.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

